Classification of Chiloscyllium : True dogfish
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Chondrichthyes (=Elasmobranchii)
- Order :- Pleurotremata(=squali)
- Family :- Scyllidae
- Genus :- Chiloscyllium
Geographical distribution of Chiloscyllium : True dogfish
Chiloscyllium is abundantly distributed in temperate and tropical sea water. It ranges from Cape of Good Hope to Indian Ocean, Australia, China and Japan. Lower Carboniferous to Recent.
Habit and habitat of Chiloscyllium : True dogfish
Chiloscyllium is a marine shark, found at a depth of about 400 fathoms.
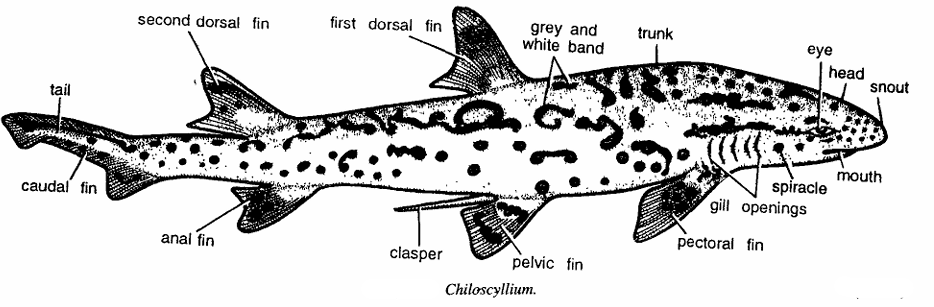
General Characteristics of Chiloscyllium : True dogfish
- Commonly called as true dogfish of moderate size.
- Body is laterally compressed and differentiated into head, trunk and tail.
- Surface of body is mottled with grey and white bands.
- Head is produced into snout and comprises ventral mouth, nostrils and eyes without nictitating membrane. Spiracle and gill openings are found behind eyes.
- Mouth contains small teeth provided with median cusps.
- Median fin consists of first and second dorsal fins are found behind pelvic and anal fins, respectively. Paired fins are pectoral and pelvic.
- Tail is very slightly curved upwards and possess caudal fin.
- It is sexually dimorphic. Males have claspers which act as intromittent organ. Fertilization internal.
- It is oviparous. Egg-case is large, quardrate and with tendrils for attachment.
Economic importance
- Very important to fisheries as its liver contains oil rich in Vitamin A.
Special features
This fish secretes Mermaid’s purse or case. The eggs are extremely yolky and as they pass down the oviduct, become surrounded by watery albumen and then by horny mermaid’s case. Each case is roughly rectangular with four long coiled filaments. Females lay egg cases among sea weeds. The filaments of the egg cases become entangled with the sea weeds soon after their emergence from the cloaca. In this condition they remain as such till the young ones come out.

Identification
Since this fish has grey and white bands and above features, hence it is Chiloscyllium


