Sphyrna is a genus of hammerhead sharks widely distributed in the world’s oceans. Members of the family tend to live in coastal waters along the intertidal zone rather than in the open ocean, as prey such as invertebrates, fish, rays, small crustaceans, and other benthic organisms are hidden in the sand and sediments of these areas. Members of the Sphyrna family are also known by synonyms such as Zygaena, Sestracion, and Sphyrichthys. The first species of this genus was Sphyrna zygaena, described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, and the last member, Sphyrna alleni, was described in 2024.
Classification of Sphyrna : Hammer headed Shark
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Chondrichthyes (=Elasmobranchii)
- Order :- Pleurotremata(=squali)
- Family :- Scyllidae
- Genus :- Sphyrna
Geographical distribution of Sphyrna : Hammer-headed Shark
Sphyrna is found in all tropical and sub-tropical sea waters and Pacific Ocean, primarily in warm coastal waters. Lower Carboniferous to Recent.
Habit and habitat of Sphyrna : Hammer-headed Shark
Sphyrna or Zygaena or Reniceps is a common marine fish, adapted for deep sea waters. It is a voracious feeder and active swimmer. It eats small fishes, but because of its attacks on man, it is dreaded as man-eater.
General Characteristics of Sphyrna : Hammer-headed Shark
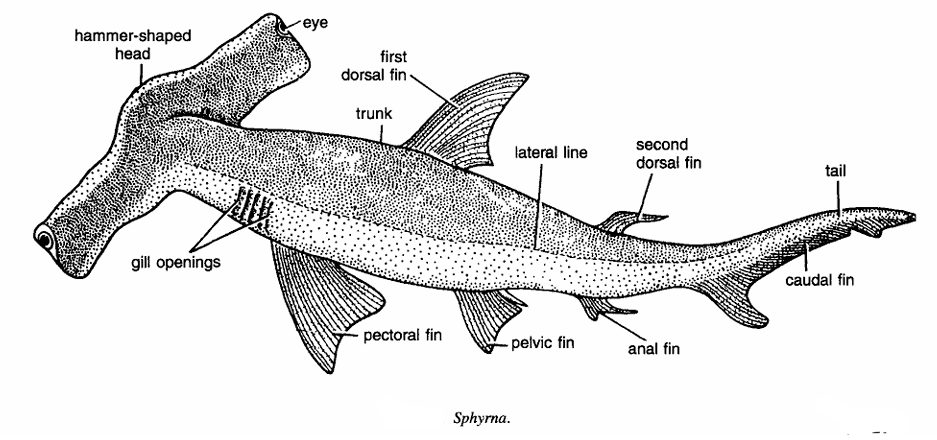
- Commonly called as hammer-headed shark due to the hammer-shaped head, which is produced into two prominent lateral lobes supported by corresponding cartrilaginous outgrowths from post-orbital or lateral ethmoidal regions of skull. Eyes containing nictitating membrane are placed at the distal extremities of the lateral lobes.
- Elongated body measuring 4 to 5 metres is divided into head, trunk and tail. The tail is raised upwards and contains caudal fin.
- Dorsal side is greyish while ventral side is yellowish.
- First dorsal fin is situated in front of pelvic fin and second dorsal fin opposite to anal rm. Both fins are devoid of spines. Pectoral fin near gill openings. Mouth is crescentic and ventral in position.
- Gill-slits 5 pairs and lateral in position. Spiracles are absent. Lateral line distinct.
- Vertebrae asterospondylus.
- Viviparous and produces about 40 young ones.
Special features
Hammer headed sharks are closely related to carcharhininae but differ in many cranial characters associated with sphyrnid cephalic ‘hydrofoil or hammer.’ Large sharks are highly dangerous and there are many records of fatal attacks on humans. S. zygaena, S. blochi, S. tiburo are some common species.

Identification
Since this fish has hammer-shaped head and above features, hence it is Sphyrna.
