Classification of Hyla : Tree Frog
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Amphibia (Cold blooded. Scaleless glandular skin. Can live in water and land. Two occipital condyles, Heart three chambered)
- Order :- Anura or Salientia (Scaleless Amphibia. Tail, external gills and gill-silts absent. Both hind limbs and forelimbs well developed.)
- Suborder :- Procoela
- Family :- Hylidae
- Genus :- Hyla
Geographical distribution
They are is commonly distributed in India, China, United States, Africa and Canada. Miocene.
Habit and habitat
They are arboreal in habit, living on trees and rocks.
General Characteristics of Hyla : Tree Frog
- Commonly known as tree frog.
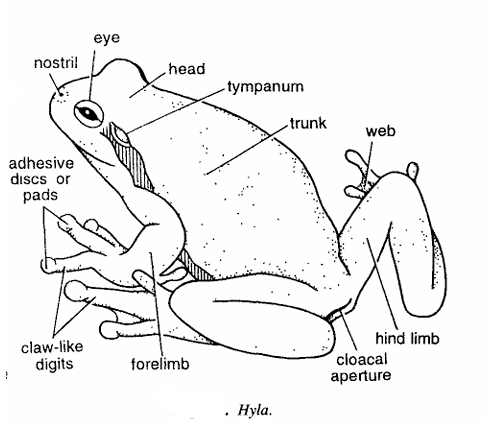
- Body measuring 3 to 8 cm in size and divided into head and trunk.
- Head contains eyes and nostrils. Forelimbs and hind limbs adapted for arboreal life.
- Terminal base of each digit is claw shaped and toes contain expanded adhesive discs or cushions which are used to climb trees.
- Eyes well developed with horizontal pupil. Tympanum distinct. Voice often loud.
- Skin of belly contains hygroscopic glands which help in adhering the frog with leaf, twigs or stem.
- Upper jaw toothed, lower jaw without teeth (edentulus).
- Transverse processes of sacral vertebra are dilated.
- Fertilization external. Eggs are laid in water. Development includes tadpole larva.
Special features
- Hyla arborea, Hyla versicolour and Hyla regita, etc., are all tree-living frogs, and adapted from amphibious to arboreal life. They also change their colour according to their environment and show camouflage or mimicry. Hyla faber shows peculiar parental care. It comes down from the tree. Females dig up mud of shallow pond, make small nurseries, and eggs are laid in them. The larvae hatch and go into submerged water.
Identification
Since this Anura contains adhesive discs in limb toes and above features, hence it is Hyla.




Pingback: Amphibians | Characteristics, Life Cycle, & Facts | Zoologyverse | 2025