Classification of Columba livia (Pigeon)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Aves (Biped and feathered vertebrates.)
- Sub Class :- Neornithes (True birds. Metacarpals fused.)
- Super Order :- Neognathae (Modern birds. no teeth. sternum keeled.)
- Order :- Columbiformes (Bill short and slender)
- Genus :- Columba
- Species :- livia
Geographical distribution
Columba is commonly found in India, forested zone of the Pacific coast and United States. Eocene to Recent.
Habit and habitat
Columba livia is the most common and familiar bird around man, nesting in buildings, old houses, warehouses, sheds and railway stations. Their flight is swift and strong. Breeding continues throughout the year.
General Characteristics of Columba livia (Pigeon)
- Commonly called as blue-rock pigeon.
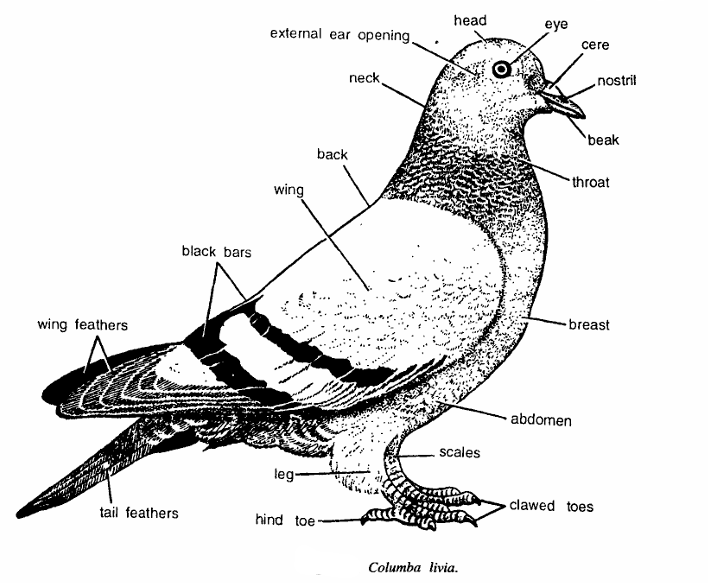
- Body is divisible into head, neck, back and breast and abdomen. Plumage is grey with glistening metallic green and purple on breast and neck.
- Head contains large eyes and slit-like nostrils.
- It is produced into a short and slender bill or beak.
- Upper and lower beaks are covered by the horny sheath, called rhamphotheca.
- At the base of the upper beaks there is a patch of skin called cere.
- Beak adapted for seed-eating.
- Eyes are large, rounded, with a well-developed nictitating membrane and a rounded pupil.
- Forelimbs are modified into wings which contain besides skeleton flight feathers called as remiges.
- Feet are covered with epidermal scutes formed by the fusion of several reptilian epidermal scales.
- Hind limbs are modified for bipedal locomotion.
- Tarsus usually shorter than toes. Wing feathers, tail feathers present.
- Other structures seen are neck, breast, abdomen and black bars on wings. Eggs white and unmarked.
Special Features
: Pigeons are the most common domesticated birds, which were in olden times used as messengers. They are also eaten by man. Their call notes are very familiar to man as gootr-goon, gootr-goon. Pigeons serve as an excellent example for artificial selection of Darwins theory of evolution as various varieties have been produced by man. Crop large, producing ‘pigeon milk’ to feed small young
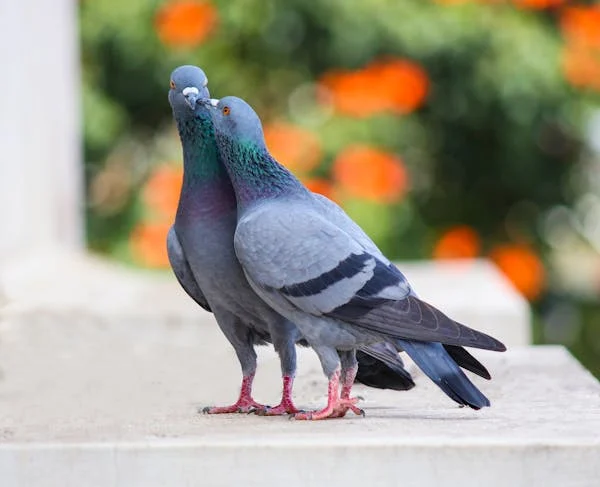

Identification
Since this bird has slaty grey plumage and above features, hence it is Columba livia.



Pingback: DISSECTION OF PIGEON | Zoologyverse | 2024
Pingback: HIPPOCAMPUS (SEA HORSE) | Zoologyverse | 2025
Pingback: Introduction to Aves (Birds) | Zoologyverse | 2025