Macropus, derived from the ancient Greek words μακρός (makrós) meaning long'' and πούς (pous) meaningleg,” is a genus of marsupials in the order Megapoda. Two large modern land kangaroos live here. There are 13 known extinct species. The reference species is the giant kangaroo.
Classification of Macropus (Kangaroo)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Mammalia (Body covered with hairs. Females have mammary glands.)
- Infra Class :- Metatheria (Pouched and viviparous)
- Order :- Masupialia (females with marsupium.)
- Genus :- Macropus
Geographical distribution
- Kangaroos are found in Australia, Tasmania and New Zealand.
Habit and habitat
- Terrestrial, gregarious, herbivorous, browsing and leaping animals
General Characteristics of Macropus (Kangaroo)
- Commonly called as Kangaroo.
- Macropus is largest Kangaroo. Males standing a maximum height of 2 meters. and weighing about 80-100 kg. Females 1.5 meters tall and 35-40 kg in weight.
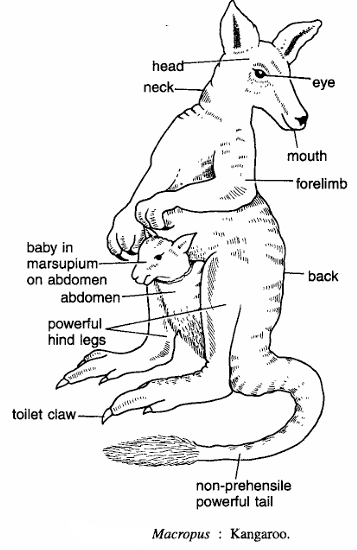
- Body divisible into head, neck, back, abdomen and tail. Head is small with large ears and eyes.
- Hind legs and feet very long and powerful, used for leaping. Forelimbs smaller.
- Hallux absent, 2nd and 3rd toes united (Syndactylus). Middle or 4th toe enormously enlarged and armed with a powerful claw. Called as toilet claw.
- Animal nearly sits on its tail during rest. The baby kangaroo is seen protruding from the marsupium on abdomen. Young one feeds on milk through teats in marsupium.
- Tail non-prehensile and powerful.
- Other kangaroos are red kangaroo and gray kangaroo.
Special features
- Kangaroos have abdominal pouch to carry young one, which is a characteristic feature of marsupials. Marsupials are mammals basically similar to Eutheria but whose youngers are born in rudimentary conditions and are generally sheltered during their later development in pouch or marsupium

Identification
- Since the animal contain marsupium and above features, hence it is Kangaroo.
