Dissection of Rat : External Features
Procedure. For external features first kill the rat with chloroform and then immerse it in a solution of lysol or any antiseptic solution. Lay the rat in a dissecting dish keeping ventral surface upwards. Note the following structures :
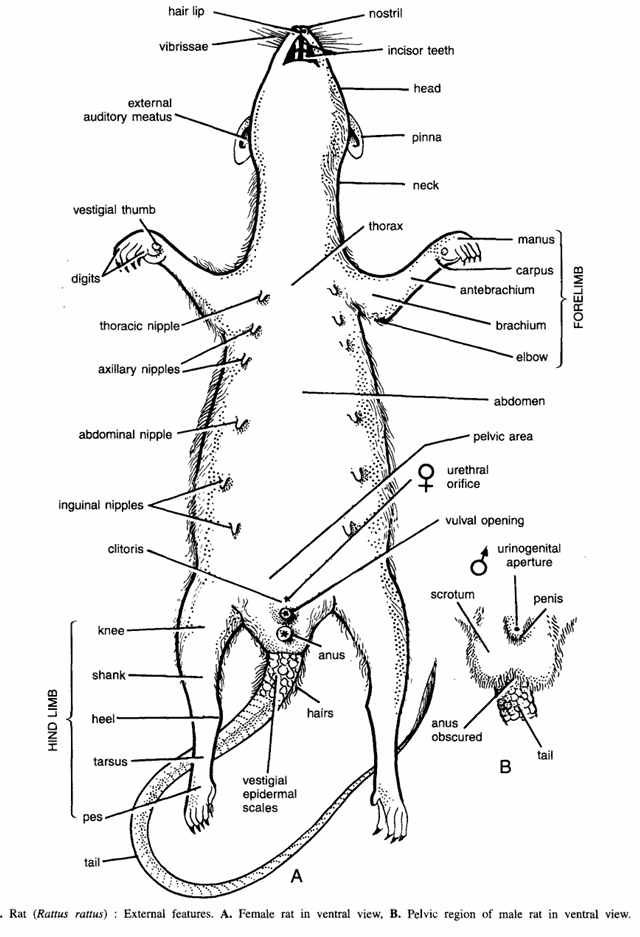
- Shape : Body is elongated and brownish in colour. Division. Entire body is regionated into the head, neck, trunk and tail. The hairs or pelages cover and protect the entire body.
- Head :- The head is elongated and somewhat conical in shape, tapering anteriorly to terminal nose. Head has the following structures :
- A pair of nostrils or nares :- They are found in front of the nose and lead into the nasal passages. Nostrils can be closed under water. Just below the nose hair like processes called in vibrissae present.
- Hairlip :- A cleft is found below the nostrils in upper lip and it exposes the two upper incisors.
- Mouth :- It is found in a sub-terminal position of the head and leads into the buccal cavity.
- Teeth :- There are 4 incisors and molars. Canines and premolars are absent. The two front incisor teeth are long and they grow throughout the life of rat. These are cutting teeth and form characteristic feature of the order Rodentia to which rat belongs. The incisor teeth are self-sharpening and chisel-like.
- Eyes :- Two, one on each side. The eyes are small. Each eyelid and a portion of cornea somewhat protrudes through the eyelids to give side vision. The external eyelid has lacrymal glands, the secretion of which keeps the eye moist. A nictitating membrane is attached to anterior cornea of each eye.
- External ears or pinnae :- These are found on the postero-Iateral area of the head.
- Neck :- It is a short region connecting the head to the body or trunk.
- Trunk :- It contains thoracic, abdominal and pelvic areas. In females, one pair of thoracic nipples 2 pairs of axillary nipples, one pair of abdominal nipples and 2 pairs of inguinal nipples are seen on ventral surface. The urethral orifice, vulval opening and anus lie close together in pelvic region. In males, there are two large testes in the scrotal sacs. The trunk region also contains forelimbs and hind limbs.
- Fore limb contains elbow, brachium, antebrachium, carpus and manus. A vestigial thumb in also seen. Hind limb is composed off knee, shank, heel tarsus and pes.
- Tail. It acts as a balancing organ. At its beginning it contains small overlapping vestigial scales.
- Size. About 25 cm including tail.
Dissection of Rat : General Anatomy
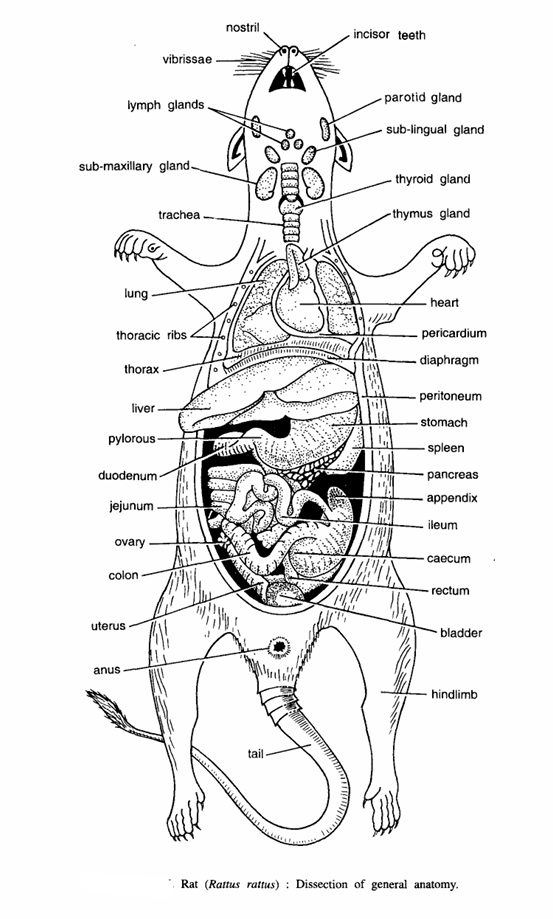
Procedure
- Kill the rat with chloroform, immerse it in any antiseptic solution and lay it on its back on the dissecting board. Fix the limbs with pin.
- Make a longitudinal slit in the skin from the pubic symphysis to the tip of the snout and make transverse cuts at the ends of longitudinal cut. Separate the skin from the muscular body wall. They are connected together by loose subcutaneous connective tissue.
- Note the presence of mammary glands in the female. Make a longitudinal incision in the abdominal wall from the pubic symphysis to xiphisternum, cut parallel to the ribs on both the sides and reflect the abdominal wall. Dissect neck region to expose the blood vessels and nerves. Expose and see various glands and organs.
- Digestive system :- It consists of :
- Mouth :- It leads into the buccal cavity, which contains teeth and tongue.
- Pharynx :- It is a chamber between the mouth and oesophagus. It acts as a common passage for food and air. It channels food into the alimentary canal and air in trachea through glottis.
- Oesophagus :- It is a short tube found just below the wind pipe.
- Stomach :- Oesophagus leads into the pear-shaped stomach, divided into cardiac and pyloric parts.
- Intestine :- Stomach leads into small intestine, which is divided into duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Colon arises from the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. The first part of colon is called as caecum, while its terminal end is called as vermiform appendix.
- Rectum :- The large intestine or rectum opens to exterior by anus.
- Associated glands
- Salivary glands :- Three pairs of these are found in buccal cavity. They secrete saliva.
- Submaxillary salivary glands :- The largest of three pairs are found on the ventral surface of the neck from the point of the jaw to the manubrium of the sternum. Their ducts open at the base of the incisors.
- Sublingual salivary glands :- They are found on the sides of the submaxillary glands and pour their secretion under the tongue.
- Paratoid salivary glands :- They are found behind and below the bases of the ears on ventro-lateral surface of the neck.
- Thymus and thyroid glands :- These are endocrine glands.
- Liver :- It is composed of four lobes.
- Pancreas :- It is also an endocrine gland. suspended by delicate mesenteries between the stomach and the duodenum.
- Heart :-It lies in pericardium and is composed of 2 auricles and 2 ventricles.
Dissection of Rat : Venous System
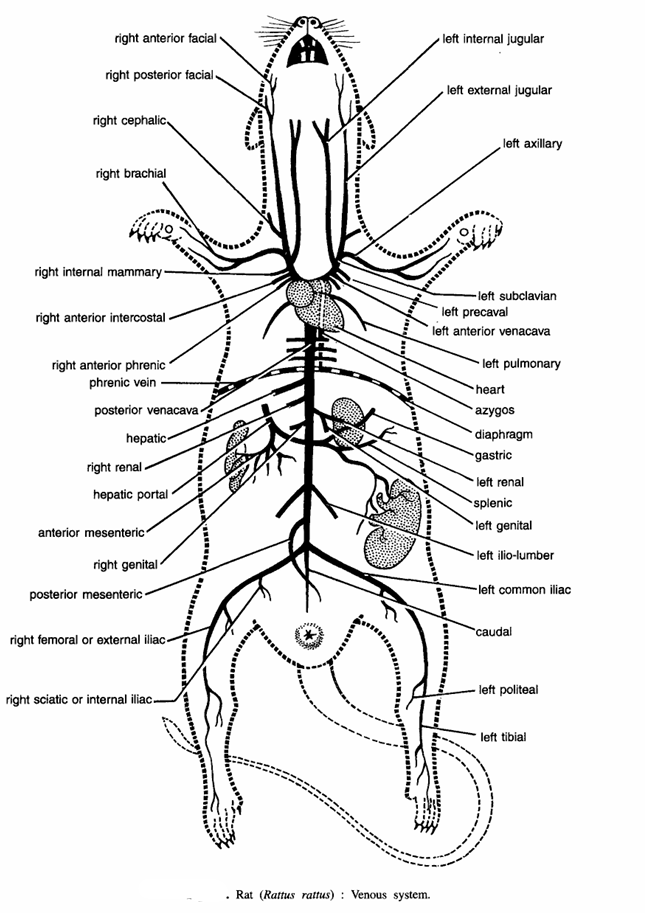
The blood from the entire body is collected by the following veins :
- A pair of pulmonary veins :-They carry oxygenated blood from lungs to the left auricle.
- A pair of precaval veins. These collect blood from the anterior body. Each precaval comprises of:
- Jugular veins :- It divides into two:
- Right and left external jugular veins :- It collects blood from lower jaw. Both right and left external jugular collect blood from face by following veins (a)Right anterior facial and left anterior facial, (b) Right posterior facial and left posterior facial, (c) Right and left cephalic veins.
- Right and left internal jugulars :- It collects blood from the brain. It joins with external jugular.
- Right and left subclavian veins :- It collects blood from forelimb and opens into precaval vein.
- Right and left anterior intercoastal veins :- It collects blood from intercoastal spaces and opens into precaval vein.
- Right and left internal mammary veins :- It collects blood from inner surface of the ventral thoracic wall and mammary glands.
- Phrenic vein :- It collects blood from the diaphragm.
- Jugular veins :- It divides into two:
- Postcaval vein :- It collects blood from the posterior part of the body by the following veins
- Caudal vein :- It collects blood from the tail.
- Right and left of iliac veins :- Each iliac vein divides into right and left femoral vein which collects blood from the outer side of the leg and right and left sciatic vein which collects blood from the inner side of the leg. The two iliac veins join with the postcaval.
- Right and left ilio-lumbar veins :- They collect blood from the lumbar region.
- Right and left posterior mesenteric vein :- It collects blood from the large intestine.
- Right and left genital veins :- They collect blood from gonads.
- Right and left anterior mesenetric vein :- It collects blood from the anterior gut.
- Hepatic portal vein :- It comprises of the following veins :
- Gastric vein :- It collects blood from the stomach.
- Anterior mesenteric :- It collects blood from the ileum.
- Splenic :- It collects blood from the spleen.
- Posterior mesenteric :- It collects blood from the large intestine.
- Right and left renal veins :- The hepatic portal vein opens into the liver.
Dissection of Rat : Arterial System
Arteries distribute blood to various parts of the body. Procedure. First locate the origin of the systemic aorta. It originates from the left ventricle, passes dorsal to the pulmonary arch and curves round to the dorsal side of the heart and lies ventral to the vertebral column, where it extends backwards as dorsal aorta. The systemic arch distributes blood to the anterior region, while the dorsal aorta to the posterior region. The arteries are
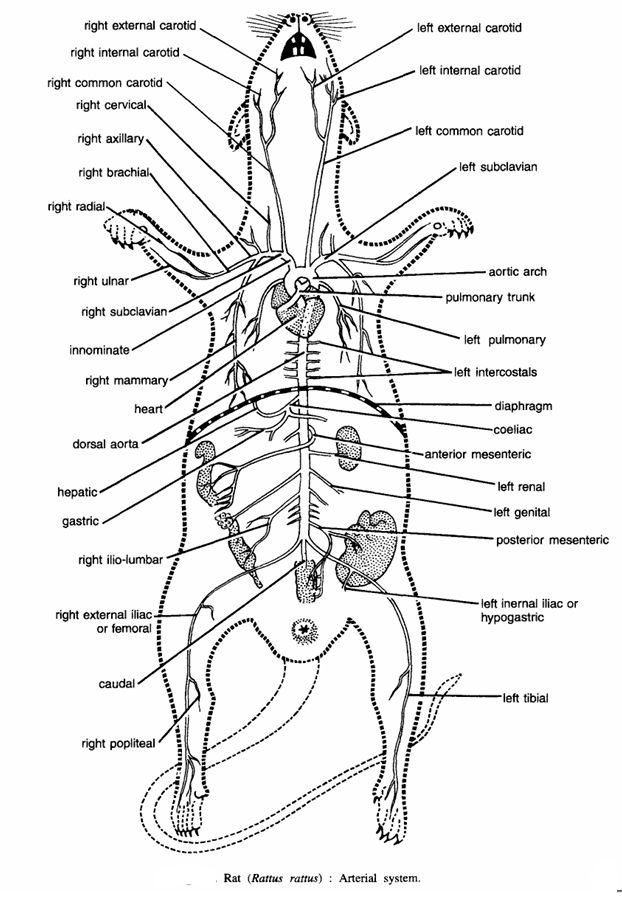
- Pulmonary arteries :- They carry de-oxygenated blood to lungs. The pulmonary arteries are given by pulmonary aorta, which originates from the right ventricle and curves over on the dorsal side of the heart.
- Systemic aorta :- It gives the following branches :
- Innominate artery. On each side right and left innominate arteries divide into
- Right and left sub-clavius and
- Right and left carotid arteries.
- The sub-clavian artery further divides into
- Right and left cervical artery.
- Right and left auxiliary artery.
- Right brachial artery and left brachial artery.
- Right vertebral artery and left vertebral artery.
- Right radial artery and left radial artery.
- Right internal mammary artery and left internal mammary artery.
- The left subclavian artery arises directly from the systemic arch and supplies to shoulder girdle and arms. Its branches correspond to the right sub-clavian.
- The right carotid artery proceeds forwards along the trachea and near the angle of jaws it divides into the right internal carotid supplying to the brain, and the right external carotid, supplying the right side of the head and face. The left common carotid artery directly originates from the systemic arch and divides into left internal carotid and left external carotid branches.
- Dorsal aorta :- It comprises of the following arteries :
- Right and left intercostal arteries. They are in several pairs supplying to the wall, of the chest.
- Right and left coeliac arteries. It gives two branches. The hepatic artery supplies to the liver and the lienogastric artery supplies to the stomach and spleen.
- Right and left anterior mesenteric artery. It supplies to the intestine.
- Right and left two gonadial arteries supply to gonads.
- Right and left a pair of renal arteries supply to two kidneys.
- Right and left posterior mesenteric artery. It supplies to the rectum.
- Right and left a pair of ilio-lumbar arteries. They supply to the body wall.
- Right and left common iliac arteries. On each side, each common iliac originates in the pelvic region and divides into internal iliac and external iliac, which supply to the legs, and vesicle artery supplying to the urinary bladder.
- Caudal artery. The dorsal aorta continues into tail as caudal artery.
Dissection of Rat: Male Urinogenital System
Procedure :- For urinogenital system cut the sides of the pubic symphysis and remove the cut portion so as to expose the posterior part of the urinogenital system. This system comprises of urinary and genital organs.
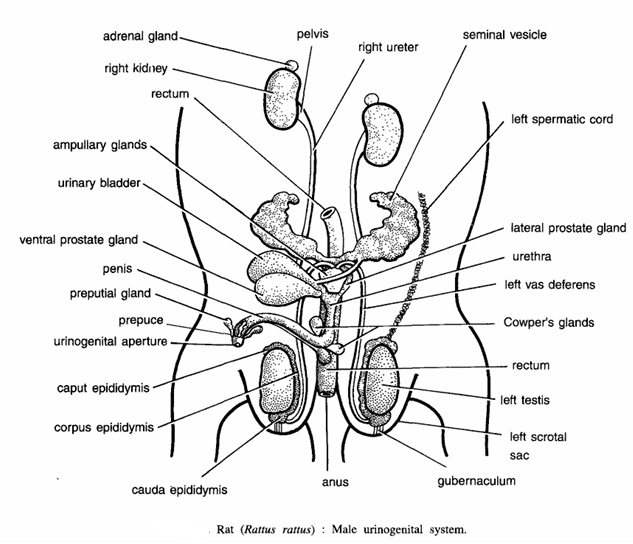
- Urinary organs or kidneys :- You have already noted the position of kidneys which are surrounded by fat. The point of attachment of kidney with ureter is called as hilus. Also observe and trace the ureter up to the urinary bladder. Remove one kidney and observe the hilus, through which the ureter and blood vessels enter and leave. With the help of a sharp scalpel cut open the kidney longitudinally and note the following parts:
- Genital organs : Note the following parts :
- Testes: A pair of testes is found in the scrotal sacs (right and left). The scrotal sacs are a pair of pouches in front of the anus and between the hind legs. The testes can be exposed by cutting the scrotal sacs. Each testis is elongated and ovoid body attached to the hinder end of the scrotal sacs by band of tissues called gubernaculum. In the very infant rat the testes lie in the abdomen close to the kidneys and just before maturity, they descend into the scrotal sacs along the inguinal canals.
- Epididymis :- It is an irregular and in the middle corpus epididymis convoluted tube, found along the inner edge of testis. At anterior end it forms caput epididymis and at posterior end cauda epididymis. Cauda epididymis gives rise to vas deferens.
- Vas deferens :- Each vas deferens coils round the ureter from the outside before opening into the urethra behind the urinary bladder.
- Urethra. It is the common duct for urine and sperms opening into the penis.
- Penis :- It is the copulatory organ through which sperms are discharged into the female genital organ, i.e., vagina of the female. The urethra opens at the tip of the penis by a slit-like opening. The tip of the penis is covered by loose skin called prepuce.
- Spermatic cord :- It is an elongated cord-like structure made up by connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves, which originate from the caput epididymis and running to the body cavity through inguinal canal.
- Accessory gland :- The following glands are associated with male genital system :
- Ampullar glands : The outer end of the vas deferens near the entrance into the urethra is enlarged into the ampulla, which contains ampullar glands to secrete mucus.
- Vesicular glands : They are branched glands originating from the vas deferens behind the ampulla.
- Prostate gland : It is a large and lobulated gland, situated just behind the junction of urinary bladder with the vasa deferentia.
- Preputial glands : They originate from the inner fold of skin forming prepuce. They secrete odorous secretion.
- Cowper’s glands :-They originate from the urethra at the base of the penis. They produce mucous secretion during sexual excitement and also protect the sperms from traces of acids found in urethra.
- Seminal vesicle :- A pair of seminal vesicle which open into urethera by a common duct other structures seen are right and left kidneys, adrenal gland, right water, left ureter, pelvis, rectum and anus.
Dissection of Rat: Female Urinogenital System
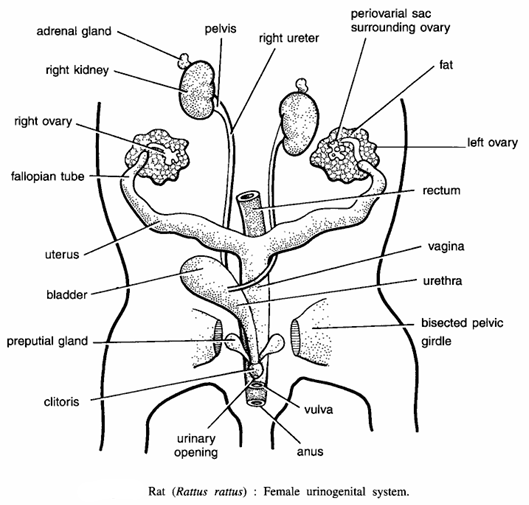
- Urinary system :-It consists of kidneys, ureters and urinary bladder, which are like those of male. The urethra is an elongated tube running towards the posterior side, opening separately at the tip of the clitoris.
- Reproductive system :- It has the following parts :
- Right and left ovaries :- There is a pair of small yellowish, compact structures like pea on the outer sides of the kidneys and are suspended in the body cavity by mesovarium. Each ovary is surrounded by periovarian sac.
- Fallopian tubes :- They are coiled and convoluted tubes. Their anterior ends form oviducal funnels.
- Uteri :- The posterior ends of the fallopian tubes become thickened to form uteri. Uteri open into vagina.
- Vagina :- It is a common chamber formed by the union of the two uteri. It serves as copulatory chamber. It opens to the exterior by a slit-like opening called vulva.
- Clitoris :- It is a rod-like structure, found anterior to vulva.
- Accessory glands :- They are found only in the uterus consisting of :
- Uterine and vestibular glands.
- Bartholi’s glands :- These correspond with Cowper’s glands of male and are related to urinogenital passage.
- Preputial glands :- These are large glands opening near the tip of clitoris.
Dissection of Rat Muscles, Blood Vessels and Nerves of Neck Region
Muscles
Remove the skin of the neck and note the following muscles
- Digastric muscles.
- Sternohyoid muscles :-Hyoid to manubrium.
- Omohyoid muscles.
- Masseter muscles.
- Sternomastoid muscles – Manubrium to skull.
- Cleidomastoid muscles – Clavicle to skull.
- Clavotrapezius muscles – Clavicle to skull.
- Deltoid muscles – Scapula to humerus.
- Pectoralis major – From sternum to humerus.
- Pectoralis minor – From sternum to scapula and humerus.
- Latissimus dorsi – From thoracic vertebra to humerus.
- External oblique abdominal muscle – From vertebra to pelvic girdle.
- Left deflected sternohyoid muscles – From hyoid to manubrium.
Blood vessels and trachea
For dissecting the neck region expose the hyoid. Remove hyoid only when dissection of the neck region is completed and observe the following :
- Common carotid arteries. They lie along the trachea. Note their divisions into the external and internal carotid arteries.
- Jugular veins. The external and internal jugular veins, collecting blood from skull and brain, unite with cephalic and subclavian veins to form the pre-caval.
- Trachea. It connects glottis with lungs. Anteriorly, trachea is dilated into the larynx, whose walls are supported by thyroid, arytenoid and crecoid cartilages. Note thyroid gland on either side of the larynx.
Nerves of neck region
Trace the carotid artery carefully and note the nerves lying by its side. Expose the pneumogastric nerves running on outer side.
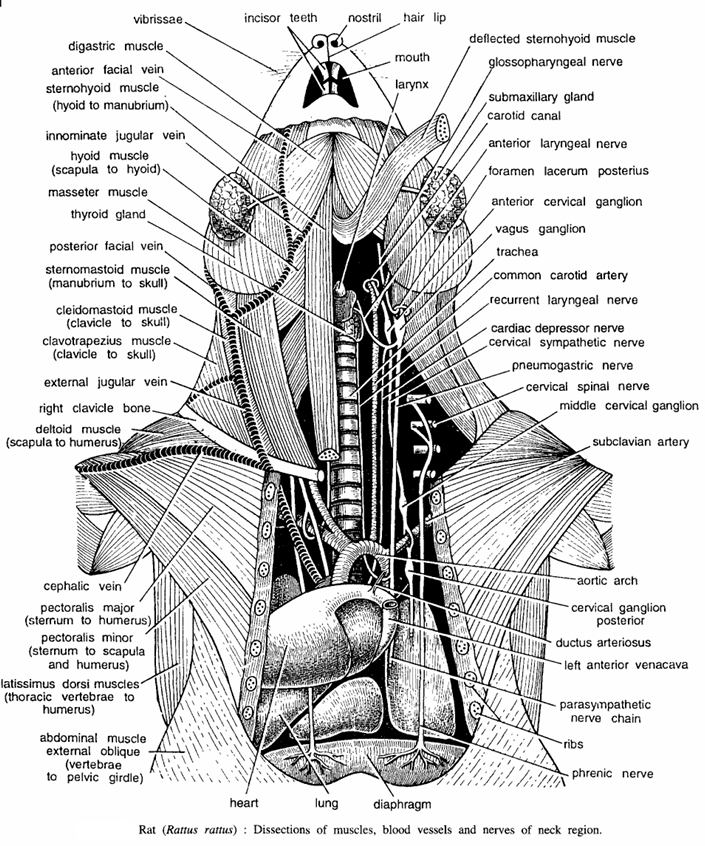
- Vagus nerve – The vagus or pneumogastric is a stout nerve containing a ganglionic swelling at its origin. It runs downwards from the foramen lacerum posterius and extends backwards along with carotid artery in the neck region.
- Anterior laryngeal nerve – It is a fine delicate nerve originating from the pneumogastric nerve from the upper border of the thyroid cartilages. It innervates the mucous membrane of the larynx.
- Depressor nerve – It is slender nerve originating form the anterior laryngeal nerve. It extends backwards along the neck dorsal to the carotid artery and it innervates heart.
- Posterior laryngeal or recurrent laryngeal – It originates from the pneumogastric nerve or vagus nerve just above the heart and it extends forwards along the side of the trachea.
- Cervical sympathetic nerve – It is a slender nerve running between the vagus and depressor nerves. It swells into ganglia both anteriorly into anterior cervical ganglion and posteriorly into the middle cervical ganglion and posterior cervical ganglia.
- Phrenic nerve :- It originates from the fourth cervical nerve and it extends backwards along the vertebral column. After passing through the thorax, phrenic nerve gives several small branches in the diaphragm.
Other structures nerve
Other structures seen are vibrissae, incisor teeth, nostril, hairtip, mouth, larynx, glassopharyngeal nerve, sub-maxillary glands, carotid canal, vagus ganglion, trachea, left anterior venacava, parasympathetic nerve chain, ribs, diaphragm heart and sub-clavi an artery.
Image Refernces :- Practical zoology Vertebrate , Dissection of Frog

