Comparative study of Vertebral Column
Scoliodon : Vertebral Column
Comments :
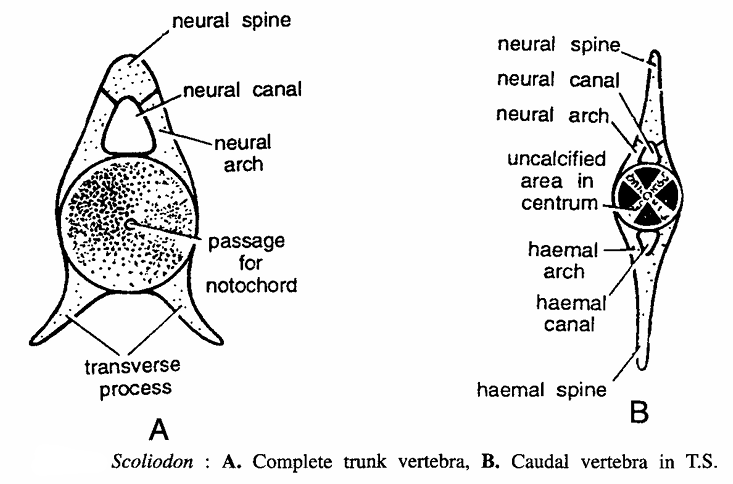
It Scoliodo Vertebral Column of 130 vertebrae divided into trunk and caudal regions. Vertebrae are amphicoelous.
- Trunk vertebra : It consists of neural spine, neural canal, neural arch, passage for notochord and transverse processes a ventral, thick, cylindrical centrum, transverse processes.
- Caudal vertebra : It differs from trunk vertebra because its transverse processes meet and fuse to form below a haemal arch enclosing a haemal canal, spine. Upper section shows neural spine, neural canal, neural arch and uncalcified area in centrum.
Vertebrae of Frog (Vertebral Column of Frog)

Comments
- Atlas (Dorsal view).
- It is a ring-shaped bone with reduced centrum on one face only.
- Anteriorly centrum contains two large concave facets for articulation with occipital condyles.
- Pre-zygapophyses absent, neural spine reduced. post-zygapophyses present and neural arch present.
- Atlas vertebra (Ventral view). It shows neural canal, post-zygapophysis centrum and anterior facet. for occipital condyle.
- Typical vertebra-2nd to 7th (Lateral view).
- It is a typical vertebra.
- It is also nearly a ring shaped bone.
- Centrum procoelous with anterior concave face and posterior convex faces.
- Neural spine is blunt and transverse processes are long and tapering on their side of centrum.
- Pre-zygapophyses (pre-zygp) are inwardly and upwardly directed, while post-zygapophyses (post-zygp) are downwardly and outwardly directed.
- The second vertebra is like other typical vertebrae except that its neural spine is short and transverse processes broad.
- Typical vertebra (posterior view). It shows neural spine, neural canal, pre-zygapophysis transverse processes and post-zygapophysis.
- Typical vertebra (Dorsal view). Structures seen are pre-zygapophysis, neural arch, post zygapophysis centrum and neural spine.
- Typical vertebra (Anterior view). It has transverse process, neural spine, post-zygapophysis, pre-zygapophysis, anterior concavity of centrum and neural canal.
- Second vertebra (Anterior view). Structures seen are neural spine, post-zygapophysis, transverse process, anterior concavity of centrum pre-zygapophysis and neural arch.
- Fourth vertebra (Anterior view). It shows neural spine, transverse process, anterior concavity of centrum and pre-zygapophysis.
- Eighth vertebra (Ventral view).
- Centrum in amphicoelus or biconcave.
- Anterior part of centrum receives posterior concavity of seventh vertebra and posterior part receives anterior convexity of ninth vertebra.
- Other structures are transverse processes, pre-zygapophysis and post-zygapophysis.
- Ninth vertebra (Ventral view). It has anterior convexity of centrum, pre-zygapophysis, iliac facet, transverse process and posterior convexity of centrum.
- Ninth vertebra (Dorsal view). Structures seen are neural spine, pre-zygapophysis, iliac facet, transverse process and posterior convexity of centrum.
- Urostyle :-
- It is the last part of vertebral column and, quite elongated.
- Centrum is rod-shaped which contains two concavities anteriorly for articulation with the ninth vertebra, and a cavity for the terminal part of the spinal cord.
Vertebrae of Varanus (Vertebral Column of Varanus)

Comments
- Vertebrae of Varanus Atlas (Anterior view)
- It is also a ring-shaped bone, composed of three pieces, two dorso-lateral and one ventral.
- Centrum and transverse processes are absent.
- During living condition, the neural canal is divided into dorsal and ventral neural canals by a ligament.
- It contains anterior concavity for occipital condyle.
- Atlas (Posterior view). Structures seen are dorso-lateral piece, dorsal neural canal, ligament, ventral neural canal and facet for odontoid process.
- Axis (Lateral view).
- It is the second cervical vertebra.
- Transverse processes are absent.
- Pre-zygapophyses reduced, while post-zygapophyses well developed.
- Neural spine large and crest-like
- Centrum contains a spine-like process below odontoid process and a hypapophysis.
- Typical cervical (Lateral view).
- Centrum elongated and strongly procoelous.
- It contains a ventral backwardly-directed hypapophysis.
- Neural spine is crest-like.
- Neural arch contains a pair of anterior upwardly-directed pre-zygapophyses and a pair of posterior backwardly-directed post-zygapophyses.
- Behind third vertebra, each cervical contains a pair of lateral facets for articulation of ribs.
- Thoraco-lumber (Lateral view).
- They are larger than cervical with strongly proceolous centrum and well developed pre- and post-zygapophyses.
- Hypapophysis absent.
- At the junction of neural arch and centrum a distinct capitular facet is present to articulate with rib.
- Thoracolumber (Dorsal view). Structure seen are neural arch, pre-zygapophysis, capitular facet for rib, neural spine, post-zygapophysis and centrum.
- First sacral.
- It supports pelvic girdle.
- Centrum is procoelous.
- Pre-and post-zygapophyses well developed.
- Neural spine slightly crest-like.
- Transverse processes greatly expanded and notched to articulate with ilia.
- Second sacral (Lateral view).
- It resembles first sacral in having procoelous centrum, low crest like neural spine neural notch and well-developed pre- and post-zygapophyses.
- It differs from first sacral in the absence of a notch in transverse processes.
- Anterior caudal
- It is like sacral superficially, but it contains a long centrum, slender neural spine and transverse processes and fairly developed pre- and post-zygapophyses.
- Specific feature of the vertebra is the presence of a Y -shaped chevron bone beneath centrum.
Vertebrae of Fowl (Vertebral Column of Fowl)
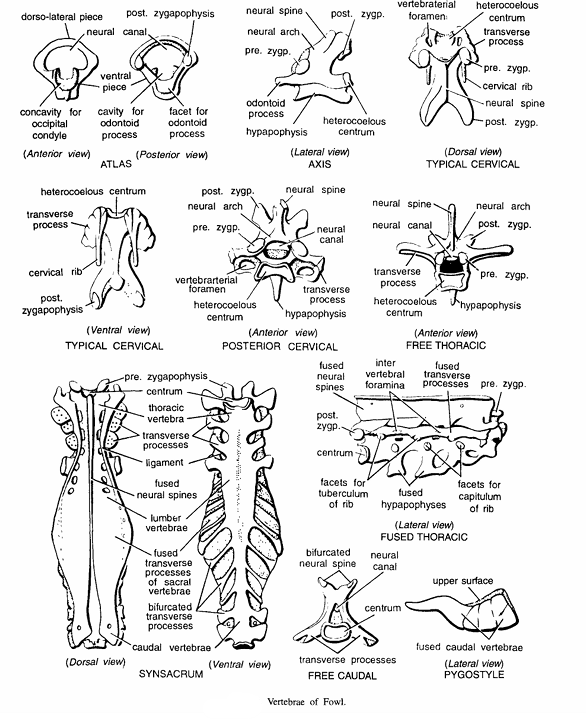
Comments
- Study of Bones Atlas
- Atlas or first cervical is ring-shaped, roughly triangular bone, composed of two dorso-Iateral and one ventral pieces.
- Concavity for occipital condyle and a notch for odontoid process.
- Centrum, neural spine, ribs, transverse processes and pre-zygapophyses are absent.
- Atlas (Ventral view) :- Structures seen are post-zygapophyses, neural canal, ventral piece, cavity for occipital condyle and facet for odontoid process.
- Axis or epistropheus
- It is also called as second cervical which is without transverse processes, ribs and vertebral canals.
- Neural spine, pre-zygapophyses and post-zygapophyses present.
- Centrum heterocoelous and produced into an anterior odontoid process.
- Typical cervical (Dorsal view)
- 14 in number.
- Centrum heterocoelous.
- Neural arch short and neural spine rudimentary.
- Transverse processes short and irregular and fused with thin, backwardly directed reduced cervical ribs.
- Pre-zygapophyses flat while post-zygapophyses project downwards and outwards.
- Typical cervical (Ventral view) :- Structures seen are heterocoelous centrum, transverse process, cervical rib and post-zygapophyses.
- Fused thoracic.
- Second to fifth 7 thoracic vertebrae are fused.
- Due to complete fusion, neural spines, transverse processes and hypapophyses look like plates which are perforated by intervertebral gaps.
- Free thoracic.
- First and sixth thoracic vertebrae are free.
- Each vertebra has heterocoelous centrum, hypapophysis and it also carries double-headed thoracic ribs.
- Posterior cervical (Anterior view). Structures seen are neural spine, neural canal, transverse hypophysis, heterocoelus centrum. vertebral enterial foramen, pre-zygapophysis neural arch and post zygapophysis.
- Free thoracic (Anterior view).
- First and sixth vertebral are free.
- Each vertebrae contains neural arch, post-zygapophysis, pre-zygapophysis, hypophysis, heterocoelus centrum transverse process, neural canal and neural spine.
- Fused thoracic (Lateral view).
- Second, third, fourth, fifth and seventh vertebrae are fused together.
- Due to complete fusion, neural spines, transverse processes and hypophysis look like plates which are perforated by intervertebral gap.
- Synsacrum (Dorsal view).
- Synsacrum in formed by last thoracic, 6 lumber, 2 sacral and 7 caudal vertebrae.
- Thoracic vertebrae contain a pair of thoracic ribs.
- Lumber vertebrae are firmly fused together with free transverse process and without hypophysis.
- Sacral vertebral fused together to form bony plate.
- Other structures seen are pre-zygapophysis centrum, fused neural spine and caudal vertebra.
- Synsacrum (Ventral view). Structures seen are pre-zygapophysis, thoracic vertebra, transverse process, lumber vertebra, fused transverse process of sacral vertebrae and bifurcated transverse processes and caudal vertebra.
- Free caudal. It has bifurcated neural spine, neural canal, centrum and transverse process.
- Pygostyle. It shows upper surface and fused caudal vertebrae.
Vertebrae of Rabbit (Vertebral Column of Rabbit)

Comments :
- Atlas :-
- It is fIrst cervical and signet-ring like.
- Centrum, zygapophyses absent and neural spine rudimentary.
- On the sides are present flattened cervical ribs, the so-called transverse processes.
- Atlas (Anterior view).
- It has 2 anterior facets feroccipital condyle,
- Other structures are neural spine, neural canal, vertebral arterial canal, transverse process and neural arch.
- Atlas (Posterior view).
- Posteriorly it has facets for odontoid processes and articular facet for axis.
- Other structures are neural arch, neural spine, neural canal and vertebraterial canal.
- During living condition neural canal is divided into dorsal and ventral parts by a ligament.
- Axis (Lateral view).
- It is second cervical.
- Neural spine is flattened, antero-posteriorly elongated and ridge-like.
- Cervical ribs or so-called transverse processes are small.
- Centrum contains peg-like odontoid process.
- Pre-zygapophyses absent. Other structures are neural arch, articular surface for atlas and post-zygapophysis.
- Typical cervical (Anterior view).
- Rest of the cervicals are typical having small neural spine, large neural arch, flattened centrum, pre-zygapophyses and post-zygapophyses.
- Transverse process bifurcated and perforated by a vertebraterial canal and facet for cervical rib present.
- Anterior thoracic (Anterior view).
- It contains a backwardly-oriented neural spine.
- Neural arch upwardly-directed pre-zygapophyses and downwardly-directed post-zygapophyses.
- Transverse processes short and contain facets for tuberculum of ribs.
- Centrum short.
- Anterior thoracic (Lateral view). Structures seen are long tilted neural spine, facets of tuberculum of rib post-zygapophysis, centrum, post-zygapophysis, intervertebral notch, centrum and pre-zygapophysis.
- Posterior thoracic (Lateral view).
- Last 4 or 5 thoracic vertebrae differ from anterior ones in having a long centrum, short neural spine, distinct zygapophyses and reduced transverse processes.
- It contains capitular facets, metapophyses and anapophyses. It has invertebral notch.
- Anterior lumbar (Anterior view).
- Out of 7, first two called as anterior lumbar vertebrae.
- Neural arch on either side contains an anteriorly-directed process called metapophysis which bears pre-zygapophysis, and a posteriorly and backwardly-directed anapophysis which bears post-zygapophysis. Hypophysis present.
- Posterior lumbar (Lateral view)
- 3rd to 7th vertebrae are called as posterior lumbar.
- The resemble anterior lumbar in all respects except that a ridge-like hypapophysis is prevent below centrum.
- Sacrum (Lateral view) :
- Sacral vertebrae (4 in number) are fused to form a compact bone supporting pelvis.
- The neural spines, zygapophyses and intervertebral formina are peculiar.
- Sacrum (Dorsal view) : Structures seen as neural spine, post-zygapophyses intervertebral foramen, 1st sacral vertebra, centrum, pre-zygapophysis and articular facet for ilium.
- Caudal (Dorsal view) : Structures seen, are neural spines, vertebral, post-zygapophysis, and pre-zygapophysis.

