Classification of Hemidactylus (Common House Lizard)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Reptilia (Scaly vertebrates. Right and left aortic arches present. Single condyle. Pulmonary respiration. Embryo with amnion and allantois.)
- Sub Class :- Diapsida (Skull with two temporal openings separated by post-orbital and squamosal.)
- Order :- Squamata (Lizards and snakes with horny epidermal scales or shields. Quadrate bone movable. Vertebrae procoelous. Anal opening transverse.. Vertebrae amphicentrous.)
- Sub-order :- Sauria or Lacertilia (Lizards. Body slender, limbs 4. Pterygoid in contact with quadrate. Eyelids movable.)
- Family :- Gecknoidae (Toes provided with adhesive pads.)
- Genus :- Hemidactylus
Geographical distribution
Hemidactylus has world-wide distribution and is chiefly found in India, Europe, Asia, Africa, United States of America, Sri Lanka and China.
Habit and habitat
Hemidactylus is a common house lizard found in every home. Nocturnal in habit. During winter they hibernate under wood, logs and crevices of the walls. They are adapted to walk on walls. They feed on insects and small invertebrates. It is a fast runner diapsid.
General Characteristics of Hemidactylus (Common House Lizard)
- Commonly known as wall lizard.
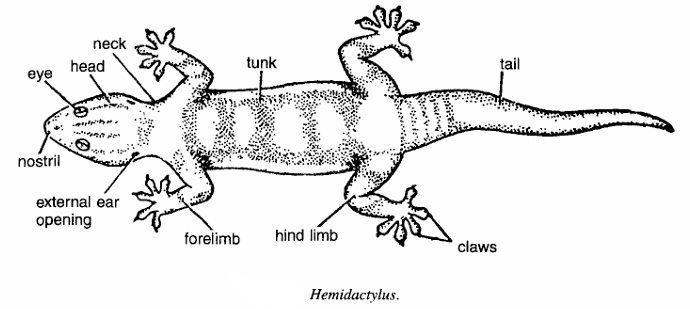
- Body measuring approximately 25 cm in length is slender, covered with minute small scales and divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
- They are ugly looking. Some members contain black and dark grey patches on dorsal surface while others have dark grey dorsal surface.
- Abdomen is yellowish white.
- Head is triangular containing eyes, nostrils and external ear opening.
- Eyes lack movable eyelids. Tongue protrusible.
- Forelimbs and hind limbs well developed. Toes are provided with rounded adhesive pads for climbing.
- Many wall lizards produce sound.
- Quadrate bone movable. Only supratemporal arch present.
- Vertebrae amphicoelous. Egg shells calcified.
Ecological Importance
Hemidactylus, a genus of geckos commonly referred to as house geckos, holds significant ecological importance in various ecosystems, including natural and urban environments. These small, nocturnal reptiles contribute to the balance of the ecosystems they inhabit through the following roles:
- Insect Population Control:
Hemidactylus geckos are voracious predators of insects, including mosquitoes, flies, moths, and cockroaches. By preying on these insects, they help regulate pest populations, benefiting both natural ecosystems and human settlements by reducing the spread of insect-borne diseases and crop damage. - Food Web Dynamics:
As both predators and prey, Hemidactylus geckos play a crucial role in the food web. They serve as an important food source for larger predators, such as snakes, birds, and small mammals, maintaining the balance of predator-prey relationships in their ecosystems. - Seed Dispersal:
Some species of Hemidactylus are known to consume fruits or nectar, indirectly aiding in seed dispersal and pollination. This activity supports plant regeneration and biodiversity in their habitats. - Adaptability and Ecosystem Integration:
Their ability to thrive in diverse environments, from forests to urban areas, allows them to contribute to ecological processes across a wide range of habitats. In urban settings, they play a role in maintaining ecological functions that might otherwise be disrupted by human activity. - Indicator of Ecosystem Health:
The presence and population trends of Hemidactylus species can serve as indicators of environmental health. As they are sensitive to changes in habitat quality and pollution, their abundance or decline can provide clues about ecosystem stability. - Biodiversity Support:
By participating in various ecological interactions, Hemidactylus geckos contribute to the overall biodiversity of their habitats. They coexist with other species, sharing resources and influencing community dynamics. - Scientific and Educational Importance:
Hemidactylus species are commonly used in studies related to herpetology, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Their widespread distribution and adaptability make them an excellent model for understanding species interactions, adaptation, and urban ecology. - Pest Control Services:
In agricultural regions, their predation on crop-damaging insects helps reduce reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting environmentally friendly pest control methods.
Overall, Hemidactylus geckos are integral to the ecosystems they inhabit, contributing to insect control, biodiversity, and ecosystem health. Their ecological roles underscore the importance of conserving their populations and habitats to maintain balanced and functional ecosystems.
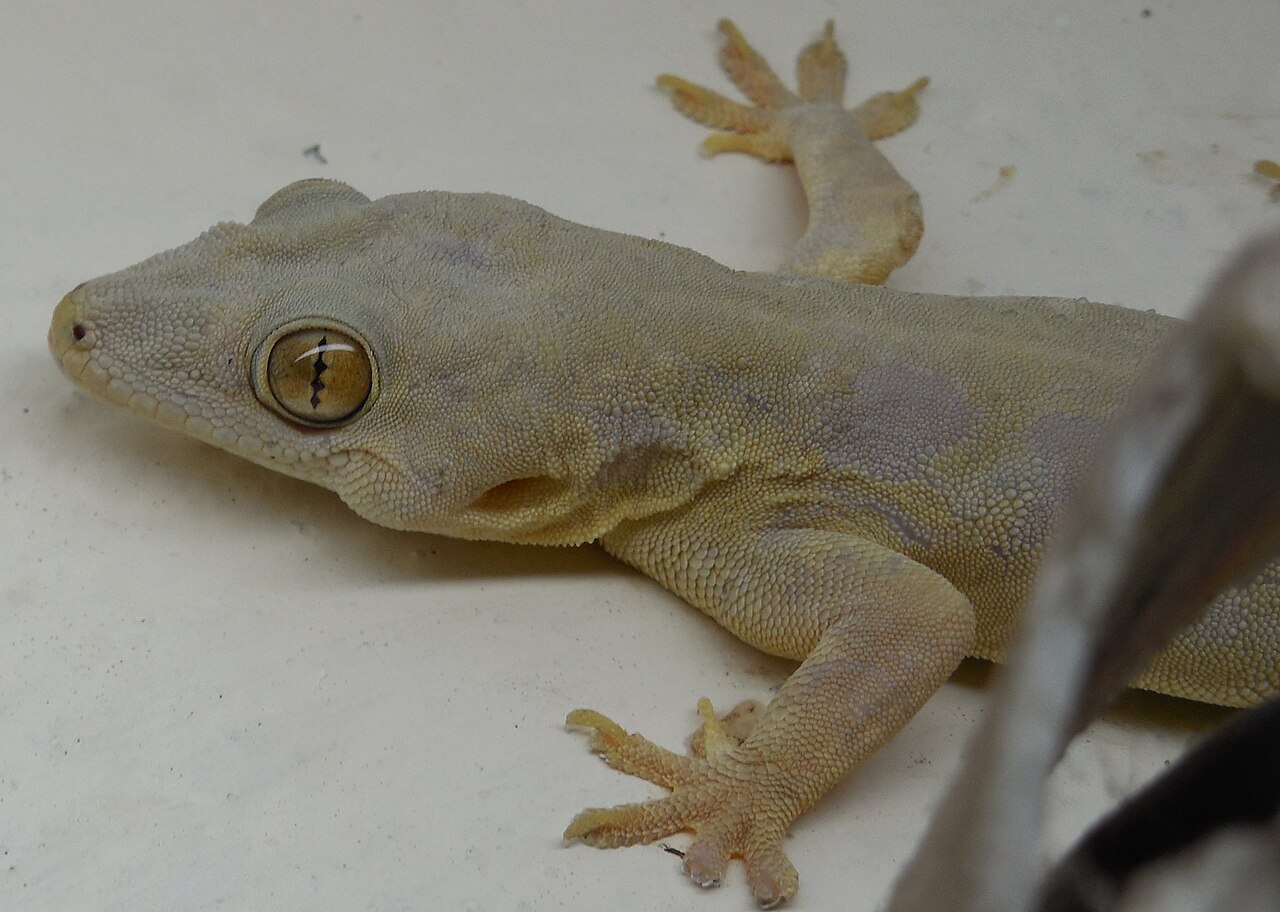

Special Features
The tail if broken from any place it again regenerates, although small in size because vertebrae jo not regenerate. Tail contains intervening unossified zones between vertebrae which are easily broken and then regenerated. This is called as caudal autotomy. Wall lizard is adapted to walk on walls, roofs and on smooth surfaces. The walking is effected by the dilated digits, which contain double series of lamellae and work under vacuum principle. The digits are first pressed over wall and then released gently to create a vacuum, by which they remain adhered to wall and are able to walk.
Identification
- Wall lizard or Hemidactylus is well familiar even to a lay-man and can easily be identified by above features.



Pingback: GECKO (WALL LIZARD) | Zoologyverse | 2024