Classification of Bubo bubo (Eurasian eagle-owl)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Aves (Biped and feathered vertebrates.)
- Sub Class :- Neornithes (True birds. Metacarpals fused.)
- Super Order :- Neognathae (Modern birds. no teeth. sternum keeled.)
- Order :- Strigiformes (Head large and rounded.)
- Genus :- Bubo
- Species :- bubo
Geographical distribution
- World-wide distribution, specially found in India, Pakistan and Myanmar.
Habit and habitat
- Nocturnal bird, living in woody places and avoids heavy forests. It feeds on small mammals, rodents, birds, lizards and other animals. It hides in retreat in day.
General Characteristics of Bubo bubo (Eurasian eagle-owl)
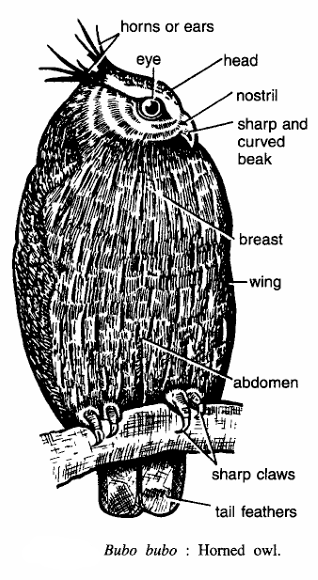
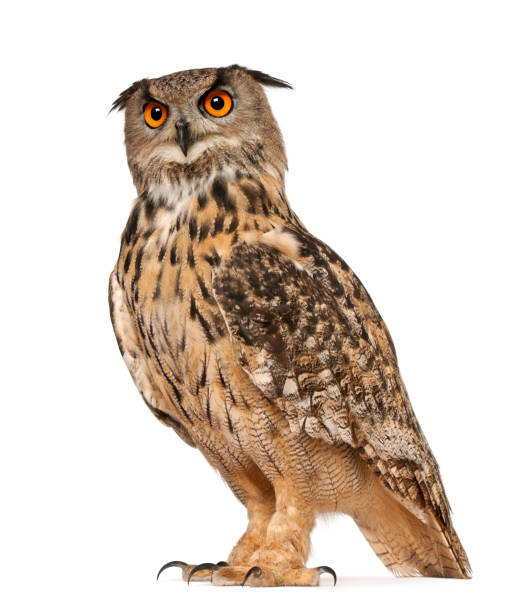
- Commonly called the Eurasian eagle owl.
- It is a fierce looking large owl with large rounded head, huge orange gold eyes and long horns or ears and nostril.
- Plumage soft textured.
- Body divided into head, back, neck, breast and abdomen.
- Bird is heavily built with dark brown back mottled and spotted with buff.
- The dark brown underside is streaked.
- Beak is short, sharp and curved and adapted for tearing and piercing.
- Eyes are large, yellow and forwardly directed, each in a disk of radial feathers.
- Wings folded over the body.
- Ear opening large, often with flap-like cover, sometimes asymmetrical.
- Legs are fully feathered. Feet adapted for grasping; claws sharp.
- Nesting season November to April.

Ecological Importance
BuBubo, a genus of owls that includes species such as the Eurasian eagle owl (Bubo bubo) and the great horned owl (Bubo virginianus), plays a significant role in maintaining ecological balance in the ecosystems they inhabit. Their ecological importance stems from their roles as apex predators, ecosystem indicators, and contributors to biodiversity.
1. Predator Role in Ecosystems
- Population Control: Bubo owls are top predators that help regulate populations of rodents, small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects. This control prevents overpopulation, reducing the risk of crop damage, disease transmission, and habitat degradation caused by prey species.
- Maintaining Food Web Balance: By preying on a variety of species, Bubo owls maintain balance within the food web, ensuring ecosystem stability.
2. Biodiversity Support
- By regulating prey populations, these owls indirectly support plant and animal diversity. For example, by controlling herbivore populations like rodents, they help prevent overgrazing and promote plant growth.
3. Scavenger Role
- While primarily hunters, some Bubo species may scavenge when food is scarce. This contributes to nutrient recycling within ecosystems by helping decompose dead animals.
4. Indicator Species
- Owls, including those in the Bubo genus, are sensitive to environmental changes such as habitat destruction, pollution, and prey availability. Their presence and health serve as indicators of ecosystem health and biodiversity.
5. Seed Dispersal Assistance
- While not directly seed dispersers, by preying on frugivorous animals, Bubo owls may indirectly influence the spread of seeds, contributing to forest regeneration and vegetation diversity.
6. Habitat Structuring
- Owls often nest in abandoned structures, cliffs, or large trees. Their nesting activities can create or maintain habitats for other species, such as smaller birds, insects, or reptiles.
7. Contribution to Scientific Understanding
- Owls provides insights into predator-prey dynamics, nocturnal ecology, and the impacts of environmental changes. This knowledge aids in conservation and ecosystem management.
Conservation Implications
- Habitat loss, human disturbances, and secondary poisoning from rodenticides are major threats to Bubo species. Conserving their habitats and ensuring prey availability are crucial for maintaining their ecological roles.
By controlling prey populations, supporting biodiversity, and serving as ecosystem health indicators, Bubo owls are vital components of the ecosystems they inhabit. Their conservation ensures the stability and functionality of these ecosystems.

Special Features
- Great economic value to mankind by destroying the harmful animals like rats and mice and these birds need careful protection.
- Soon after sunset, they produce deep soothing prolonged voice bubo. Mythologically owl is considered unauspicious. Academically Barn owl is very important as Camillo Golgi described Golgi body from nerve net of this owl..
Identification
- Since this bird has large forwardly directed eyes and above features, hence it is Bubo.


Pingback: TYPES OF BEAKS IN BIRDS | Zoologyverse | 2025
Pingback: Introduction to Aves (Birds) | Zoologyverse | 2025