Introduction
The rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) is one of the most widely recognized and studied primates in the world. Native to South, Central, and Southeast Asia, this medium-sized monkey is known for its adaptability to diverse habitats, from tropical forests to urban environments. Rhesus macaques have a significant place in ecological systems and scientific research, particularly in medical studies.
Classification of Macaca Mulatta (Rhesus Monkey)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Mammalia (Body covered with hairs. Females have mammary glands.)
- Order :- Primates (Head turns easily on neck.)
- Family :- Cercopithecidae
- Genus :- Macaca
- Species : Mulata
Geographical distribution
- Old world monkeys found in India, China, Vietnam and Asia.
Habit and habitat
- Arboreal (tree living), terrestrial, diurnal and social
General Characteristics of Macaca Mulatta
- Commonly called as Rhesus monkey.
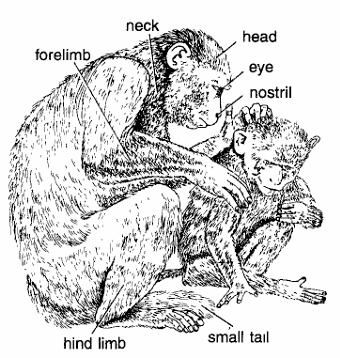
- Body divided into head, trunk, tail and abdomen.
- Head contains, mouth, eye and nostril.
- Cranium enlarged, nostrils ringed by bare skin.
- Protrusible fascial muscles permit emotional expression.
- Body covered with brownish or golden hairs.
- internal cheek pouched for storing the food.
- Buttocks contain two dried tuberosities with exposed calloused skin.
- Stomach single.
- External ear reduced. Forelimbs and hind limbs well developed.

Ecological Importance
- Seed Dispersal: Rhesus macaques consume a variety of fruits and assist in seed dispersal, which contributes to forest regeneration and plant biodiversity.
- Control of Invertebrate Populations: By feeding on insects and other invertebrates, they help control pest populations, maintaining ecological balance.
- Prey for Predators: As part of the food web, rhesus macaques are prey for larger predators like leopards, eagles, and pythons, supporting the ecosystem’s trophic dynamics.
- Ecosystem Engineers: Their activities, such as digging for roots or interacting with plants, contribute to soil aeration and nutrient cycling.
Conservation Status of Macaca Mulatta
- IUCN Red List Status: Rhesus macaques are listed as Least Concern due to their large population and adaptability. However, specific populations face localized threats.
- Threats to Survival:
- Habitat Loss: Deforestation and urbanization have reduced their natural habitats.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: In urban areas, their interactions with humans often lead to conflicts.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: Rhesus macaques are sometimes captured for the exotic pet trade or traditional medicine.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Protected Areas: They are found in several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries across their range.
- Research and Monitoring: Their populations are monitored as part of broader conservation programs.
- Community Awareness: Efforts to educate communities about coexisting with macaques help reduce human-wildlife conflict.

Special features of Macaca Mulatta
- Monkeys are famous for carricaturing. Trained monkey’s dance provides amusement to children. Rh blood factor was first discovered in monkeys which has great significance in blood transfusions.
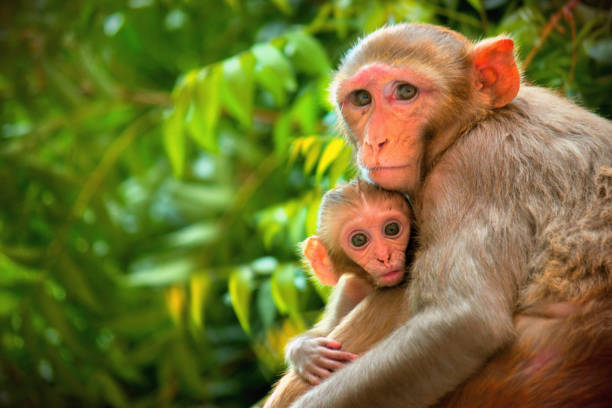
- Monkeys exhibit parental care. Other monkeys are Squirrel monkey (Saimiri), Spider monkey (Ateles), Marmoset (Callithrix) and Langur (Presbystis).
- Highly Adaptive: Rhesus macaques thrive in diverse environments, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and urban areas, showcasing their exceptional adaptability.
- Complex Social Structure: They live in hierarchical troops with intricate social dynamics, including grooming and alliances, which are essential for group cohesion.
- Scientific Importance: Macaca mulatta has been instrumental in medical and psychological research. They were pivotal in developing the polio vaccine and are used in neuroscience, behavioral studies, and genetics.
- Facial Expressions and Communication: Known for their expressive faces, they communicate through a wide range of vocalizations and gestures, reflecting their intelligence and social complexity.
- Long Lifespan: They can live up to 25 years in the wild, with even longer lifespans in captivity, making them a valuable species for longitudinal studies.
Identification
- Since the animal contains ischial tuberosities and all above features, hence it is Macaca.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) – Macaca Research
- Smithsonian’s National Zoo – Rhesus Macaque
- Reptile Database – Primates
- BBC Wildlife – Rhesus Macaques
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate