Introduction
The chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) is one of the closest living relatives to humans, sharing approximately 98-99% of our DNA. Native to the forests and savannahs of Africa, chimpanzees are highly intelligent primates known for their complex social structures and tool-use abilities. They are integral to the ecosystems they inhabit and are a symbol of wildlife conservation efforts worldwide.
Classification of Pan Triglodytes (Chimpanzee)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Mammalia (Body covered with hairs. Females have mammary glands.)
- Order :- Primates (Head turns easily on neck.)
- Family :- Hominidae
- Genus :- Pan
- Species :- triglodytes
Geographical distribution
- West African forests, Sierra Leone, Uganda and Tanganiyka.
Habit and habitat
- Arboreal but mostly lives on ground. They build nests each evening and sleep in them overnight.
General Characteristics of Pan Triglodytes (Chimpanzee)
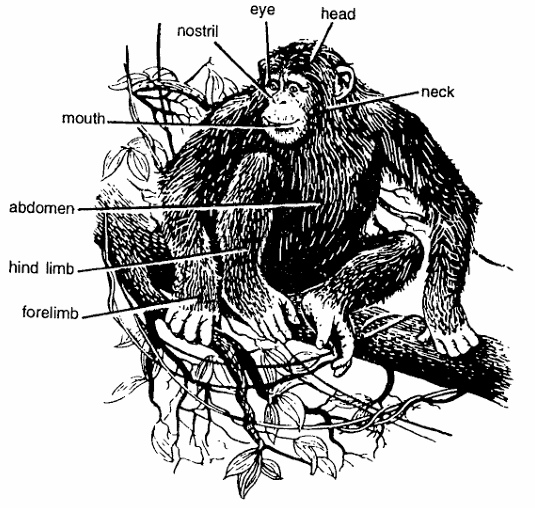
- Commonly called as Chimpanzee. Body divisible into head, neck, trunk and abdomen.
- Size 54 inches tall, weight 75-85 kg.
- Back and thigh of adults gray. Head, neck, limbs, except face, fingers and toes are covered by thick black hairs. Back is covered by grey hairs.
- Arms long and legs short. Muzzle protrudes.
- Skull prominent and rounded. Head rounded, ears large and prominent. Head contains sunkers, eyes small nose and bulging lips.
- Male has a big goitre-like throat sac and two fatty· swellings in the cheeks.
- Feeds on buds of fruits.
- Single young born and suckled for 4 years. Gestation period 225 days.
- On ground it walks on knuckles. Forelimbs and hind limbs well developed.

Ecological Importance
- Seed Dispersal: Chimpanzees consume a diverse diet, including fruits, and play a crucial role in dispersing seeds over large areas, aiding forest regeneration and biodiversity.
- Maintaining Ecosystem Balance: As omnivores, they influence populations of other species, including plants, insects, and smaller animals, contributing to ecological balance.
- Indicator Species: Their presence reflects the health of their habitat, making them a key species for monitoring ecosystem health.
- Nutrient Cycling: By feeding on a variety of plants and leaving organic matter behind, chimpanzees contribute to nutrient cycling in the soil.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List Status: Chimpanzees are classified as Endangered, with their populations declining across their range due to various threats.
- Threats to Survival:
- Habitat Loss: Logging, agriculture, and infrastructure development have significantly reduced their forest habitats.
- Hunting: Chimpanzees are hunted for bushmeat and captured for the illegal pet trade.
- Disease: Infectious diseases, including those transmitted by humans, have devastating effects on populations.
- Climate Change: Alterations in weather patterns affect food availability and habitat conditions.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Protected Areas: National parks and reserves such as Gombe Stream and Kibale protect chimpanzee habitats.
- Research and Monitoring: Long-term studies, such as those initiated by Jane Goodall, provide insights into their behavior and needs.
- Anti-Poaching Initiatives: Efforts to curb illegal hunting and trafficking are critical for their survival.
- Community Engagement: Educating local communities about the importance of conservation helps reduce human-wildlife conflict.
- International Protection: Chimpanzees are listed under CITES Appendix I, restricting their international trade.

Special features
- Tool Use and Intelligence: Chimpanzees are one of the few non-human species known to use tools. They use sticks to extract termites, stones to crack nuts, and leaves for sponges, showcasing their problem-solving abilities.
- Complex Social Structures: They live in communities with hierarchies and intricate relationships. Social bonding, grooming, and cooperation are hallmarks of their behavior.
- Communication Skills: Chimpanzees communicate using a combination of vocalizations, facial expressions, and gestures, demonstrating advanced social interaction skills.
- High Parental Care: Mothers invest years raising their offspring, teaching them vital survival skills and fostering strong emotional bonds.
- Genetic Proximity to Humans: Their close genetic relationship to humans makes them invaluable in understanding human evolution, behavior, and diseases.
Identification
- Since, the animal has bulding lips and above features, hence it is Chimpanzee.
References
- Jane Goodall Institute – Chimpanzees
- National Geographic – Chimpanzees
- Smithsonian’s National Zoo – Chimpanzee Facts
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate


Pingback: What Are Mammals? Definition, Characteristics | Zoologyverse | 2025