Introduction
Rattus rattus, commonly known as the black rat or roof rat, is a small rodent species native to the Indian subcontinent but now distributed worldwide due to human activities. Known for its adaptability, the black rat thrives in diverse environments, including urban areas, forests, and agricultural lands. While often viewed as a pest, it plays a role in ecosystems and has historical significance in human societies.
Classification of Rattus Rattus (Rat)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Mammalia (Body covered with hairs. Females have mammary glands.)
- Order :- Rodentia (Having one pair of upper incisors)
- Family: Muridae
- Genus :- Rattus
Geographical distribution
- Rattus rattus is found in all parts of the world. It prefers warmer and drier conditions. Eocene to Recent.
Habit and habitat
- It is a common rat inhabiting holes and burrows in houses and in cultivated fields. It feeds on stored grains.
General Characters of Rattus Rattus (Rat)
- Commonly called as black rat.
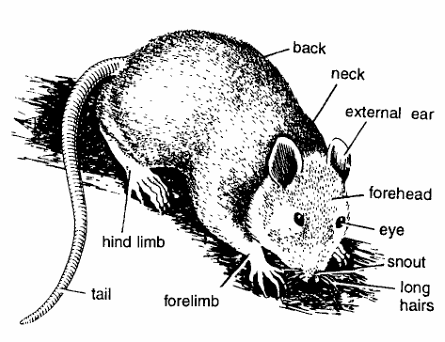
- Body divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail.
- Head contains ears, eyes, nostrils, and snout with
- long moustache or vibrissae.
- Body and limbs covered with hairs.
- Pinnae well developed. Eyes sharp.
- Tail is elongated and scaly.
- Incisor teeth chisel-like, open-rooted, used for gnawing. Canines absent.
- Viviparous

Ecological Importance
- Seed Dispersal: Black rats contribute to seed dispersal by consuming fruits and discarding seeds, aiding in plant propagation.
- Prey for Predators: They are a food source for various predators, including owls, snakes, and carnivorous mammals, playing a role in the food web.
- Ecosystem Dynamics: Their foraging behavior affects plant community structures and invertebrate populations, influencing local ecosystems.
- Indicator Species: Changes in black rat populations can indicate shifts in environmental conditions and habitat health.
Conservation Status of Rattus Rattus (Rat)
- Global IUCN Status: Least Concern. Rattus rattus is widespread and abundant due to its adaptability and association with human environments.
- Threats:
- Invasive species like the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) outcompete black rats in many regions.
- Habitat changes in wild areas can impact populations not associated with human habitats.
- Impact as an Invasive Species: In regions where it is introduced, such as islands, black rats pose significant threats to native species by preying on birds, reptiles, and invertebrates, contributing to biodiversity loss.
- Conservation Measures: Efforts focus on controlling populations in areas where they harm native biodiversity, especially on islands.

Special features
- Rat destroys the crop and stored grains. It also spreads typhus fever and plague. It acts as carrier of these diseases. Rat has great experimental value.
- It is largely used in various biophysical and biochemical studies. It also acts as intermediate host for various helminthic diseases.
- Adaptability: Black rats can thrive in diverse environments, from urban buildings to rural forests.
- Climbing Ability: Their exceptional climbing skills allow them to inhabit roofs, trees, and elevated spaces, unlike the ground-dwelling brown rat.
- Nocturnal Behavior: They are primarily active at night, using their acute senses to forage and avoid predators.
- Rapid Reproduction: Black rats have a high reproductive rate, allowing them to quickly establish populations in new areas.
- Historical Significance: They played a key role in the spread of the Bubonic Plague during the Middle Ages, as they carried plague-infected fleas.
Identification
- Since the animal has long vibrissae and above features, hence it is Rattus rattus.
References
- IUCN Red List – Rattus rattus
- National Geographic – Rats
- Animal Diversity Web – Rattus rattus
- Wikipedia – Black Rat
- Wildlife Trust – Invasive Species
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate


Pingback: EMBRYOLOGY SLIDES – RABBIT (SPERMATOGENESIS & OOGENESIS) | Zoologyverse | 2025