Introduction
Wallago attu, commonly known as the freshwater shark or wallago catfish, is a large, predatory catfish species belonging to the family Siluridae. Native to South and Southeast Asia, this fish is characterized by its elongated body, large mouth with sharp teeth, and prominent barbels. Its significant size and predatory nature make it a dominant species in its habitat.
As an important fish in aquaculture and local fisheries, Wallago attu holds economic and ecological significance. Its role as an apex predator helps maintain the ecological balance in freshwater ecosystems. However, habitat destruction, overfishing, and pollution have contributed to population declines in certain regions.
Classification of Wallago attu (Lachi)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Osteichthyes (Bony fishes. Skin contains dermal scales. Paired lateral fins present. Gills, air bladder present. Cleavage meroblastic.)
- Sub-Class :- Actinopterygii (Modern fishes. Vertebrae amphicoelous. Caudal fin homocercal, Scales cycloid or ctenoid. Nostrils do not communicate with mouth cavity.
- Superorder : Teleostei (Bony fish proper)
- Order :- Siluriformes (Anterior vertebrae fused. Weberian ossicles present between air bladder and ear.)
- Family :- Siluridae
- Genus :- Wallago
- Species :- attu
Geographical distribution
- Found across South and Southeast Asia, including countries such as India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Also reported in parts of China and Indonesia.
Habit and habitat
- Wallago is found in temperate and tropical fresh-waters, inhabiting deep flowing waters of rivers and tanks in hilly and low country regions. It is predacious and feeds on young carps.
- Habit:
- Carnivorous and predatory, feeding on smaller fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates.
- Nocturnal behavior, with increased activity during the night.
- Habitat:
- Inhabits freshwater rivers, lakes, ponds, and reservoirs.
- Prefers slow-moving or stagnant water with dense vegetation and muddy bottoms.
- Found in both clear and turbid waters, often near submerged logs or aquatic vegetation

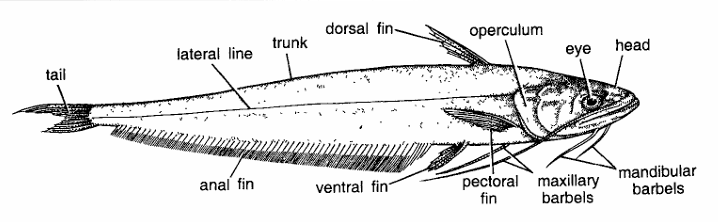
General Characteristics of Wallago attu (Lachi)
- Commonly called as cat-fish or Lachi.
- Colour of the body varies. Dorsally it is greyish brown, head is purplish and belly whitish.
- Body is divided into head, trunk and tail. Head is very large, trunk small and tail long and tapering.
- Jaws provided with villiform teeth.
- Clefts of the mouth extend behind the orbits.
- Head contains nostrils, 2 long maxillary and 2 smaller mandibular sensory barbels.
- Eyes are found above the level of the mouth and not covered with skin.
- Weberian ossicles are present. Gill membranes free.
- Dorsal fin is small like pectorals. It has fewer than seven rays and is not preceded by a spine.
- Adipose fin absent. Pectoral fin finely serrated. Anal fin large and extends upto caudal fin but not confluent with caudal fin. Caudal fin forked. Anal fin very much elongated and contains about 90 anal rays. Ventral fins small.
- Scales are absent and body is covered with naked skin. Profile of the back oblique.
Ecological Importance
- Top Predator: Regulates populations of smaller fish and aquatic organisms, maintaining ecological balance.
- Biodiversity Indicator: Sensitive to environmental changes, making it an indicator of ecosystem health.
- Nutrient Cycling: Contributes to nutrient cycling through its predatory and excretory activities.
Conservation Status
- Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN but faces localized threats.
- Major threats include:
- Habitat destruction due to dam construction and water pollution.
- Overfishing for commercial and subsistence purposes.
- Conservation measures include habitat restoration and sustainable fishing practices.
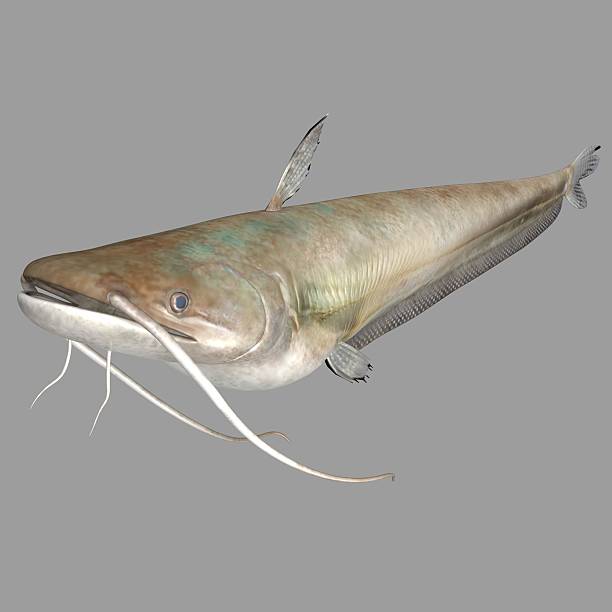

Special features
- Large Size: Can grow up to 2 meters in length, making it one of the largest freshwater catfish species.
- Adaptability: Thrives in a variety of freshwater habitats, including low-oxygen environments.
- Economic Value: Prized for its high-quality meat and significant role in local fisheries and aquaculture.
- Predatory Nature: Aggressive hunter with a wide mouth and sharp teeth, allowing it to prey on a variety of aquatic organisms.
- Breeding Behavior: Spawns during the monsoon season, with eggs deposited in vegetation-rich areas to protect offspring.
Identification
- Since this fish has smooth skin, small dorsal fin and above features, hence it is Wallago.
References
- FishBase – Wallago attu
- IUCN Red List – Wallago attu
- ResearchGate – Ecology and Behavior of Wallago attu
- World Biodiversity Database – Wallago attu
- National Fisheries Development Board (India)
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate

