Amphioxus Slides : V.L.S. Anterior Region
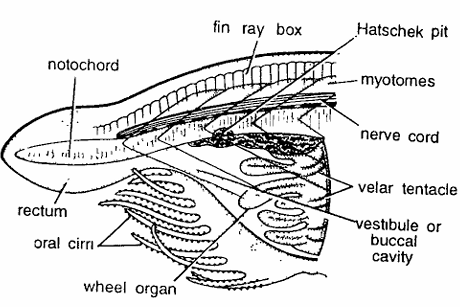
Comments
- The vertical longitudinal section shows buccal cirri, wheel organ, velum and some pharyngeal region.
- In a carmine stained section, prominent dorsal structures are fin rays, notochord and nerve cord.
- Dorsal fin is low, continuous and supported by fin rays.
- Nerve cord or spinal cord lies just above the notochord.
- It contains anterior and posterior pigmented spots and anteriorly swollen as cerebral vesicle.
- Notochord lies just above the nerve cord forming axial skeletal rod.
- It extends antero posteriorly. Anterior end projects as the rostrum.
- Important ventral structures are oral hood, vestibule, wheel organ, pharynx and atrium.
- Oral hood is clearly seen with oral cirri, which help during feeding by turning inwards to prevent sand particles from passing into buccal cavity.
- Oral hood guards the vestibule or buccal cavity.
- At the hinder wall of vestibule lies a vertical partition called velum with velar tentacles.
- In front of velum is a peculiar wheel organ which helps in driving a current of water loaded with food particles into the mouth.
Identification: Since the above section has oral cirri and all above features, hence it is Amphioxus V.L.S. region.
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Oral Hood
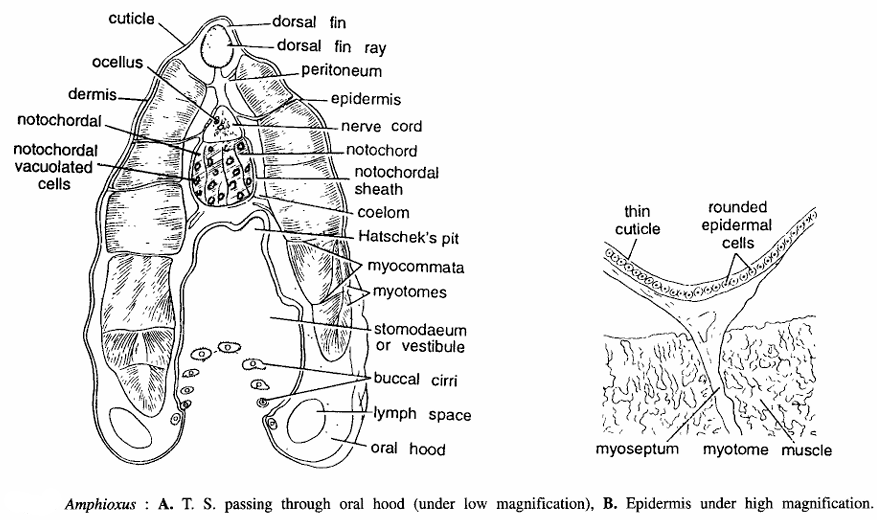
Comments
A. Under low magnification: (10 X eye-piece; 4 X objective).
- At the anterior end of Amphioxus is a mid-ventral opening encircled by frilled membrane, called oral hood.
- The T.S. Passing through the oral hood shows body wall, dorsal fin ray, nerve cord, notochord, vestibule and oral hood, etc.
- Body wall is composed of epidermis, dermis or cutis and muscle layer.
- Epidermis is covered by a non-pigmented and iridescent cuticle. Unlike other chordates, the Amphioxus epidermis is very thin.
- Dermis is indistinct. Below epidermis and dermis is a thick longitudinal muscle layer.
- The cut segmental blocks or myotomes are very distinct, separated by myosepta.
- The muscle fibers in anterior half section are directed upwards while in posterior half, backwards. Below muscle layer is coelom. Dorsally below the epidermis is a dorsal fin ray.
- Dorsal tubulated glandular nerve cord having a central canal or neurocoel and below it notochord are clearly seen.
- The notochord is composed of chordal or fibrous sheath, which encloses vacuolated notochordal cells filled with homogeneous liquid.
- Ventrally, section shows a large stomodaeum, oral hood and cut part of buccal cirri in a circular manner.
- Oral hood contains lymph spaces. Dorsal wall of buccal cavity has a sensory Hatscheck’s groove.
Under high magnification: (10 X eye-piece; 40 X objective).
- Epidermis is vary clearly seen under this magnification.
- It is composed of single layered rounded epithelial cells with some chemoreceptor cells and unicellular gland cells covered by thin cuticle. The myosepta are continuous with epidermis and visceral layer.
- Myotome muscles and myoseptum are seen.
Identification: Since the section has buccal cirri and all above features, hence it is T.S. passing through oral hood of Amphioxus.
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Pharynx
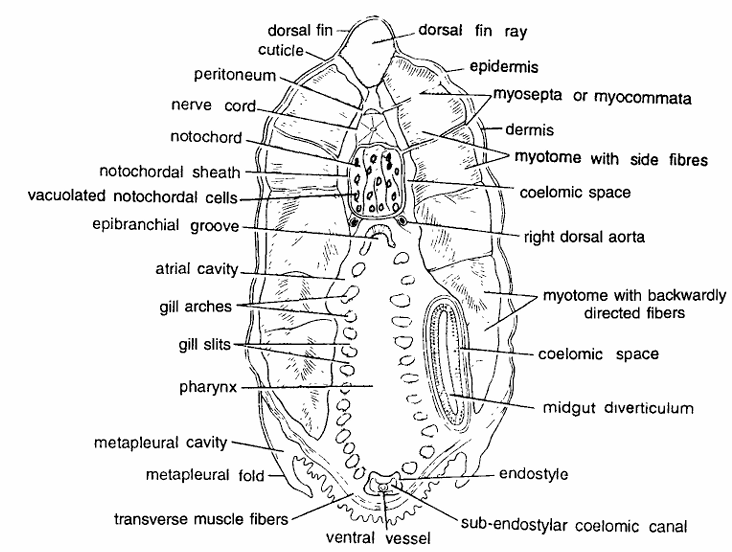
Comments
- Pharynx is a large elongated, sac-like respiratory and digestive organ, extending from behind velum upto the intestine.
- T.S. passing through anterior pharynx shows body wall layers, dorsal rm ray, nerve cord, notochord, large cut pharynx with endostyle and metapleural folds.
- Body wall is composed of cuticle, epidermis, dermis and muscle layer.
- Cuticle and epidermis are thin-layered and indistinguishable. Below epidermis the dermis is also thin-layered.
- More than three-fourth of the section from dorsal side contains thick; cut, segmental muscle bundles or myotomes separated by transverse myosepta.
- The first three myotomes have side muscle fibres whlle in posterior, half the muscle fibers are backwardly directed.
- Dorsally, just beneath epidermis, is the dorsal fin ray. Below dorsal fin ray is nerve cord and beneath nerve cord is notochord.
- Notochord is surrounded by notochordal sheath and filled with vacuolated notochordal cells.
- Ventral half of the section contains the large pharynx surrounded by atrial cavity and perforated by gill slits.
- It contains longitudinal rows of cilia in the form of an epipharyngeal groove mid-dorsally and an endostyle enclosing an endostylar canal, midventrally.
- The ciliated grooves direct food material towards oesophagus.
- The sides of the pharyngeal cavity contain several gill arches.
- Pharynx is adapted for ciliary feeding.
- Two metapleural folds with metapleural cavity are seen posteriorly.
- In some sections through pharynx, midgut diverticulum or liver is also seen.
- Other structures seen are dorsal aorta, coelomic spaces, gill arches, ventral vessel and transverse muscle fibers.
Identification: Since this section shows epipharyngeal groove, gill slits and all above features, hence it IS T.S. Amphioxus through pharynx.
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Ovaries
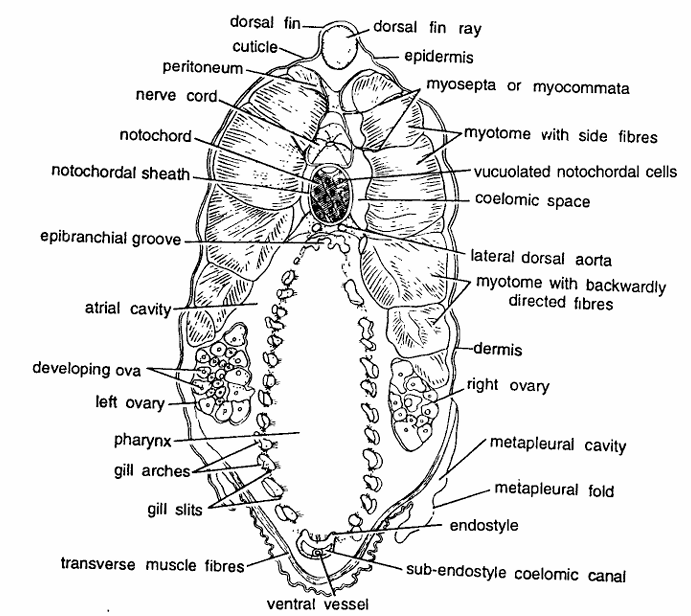
Comments
Under low magnification : (10 X eye-piece; 4 X objective).
- T.S. passing through above region shows body-wall layers, nerve cord, notochord, pharynx, midgut (liver) and ovaries.
- Body wall is composed of cuticle, epidermis, dermis and muscle layer. Cuticle, epidermis and dermis are very thin and indistinguishable.
- The musculature consisting of longitudinal fibers is well developed.
- First four segmental myotomes are thick and separated by myosepta.
- Last two myotomes are comparatively thinner.
- Muscle fibres in first three myotomes are directed sideways and upwards while muscle fibres in last three myotomes are backwardly directed.
- Dorsal tin ray is present just beneath the mid-dorsal epidermis.
- Below fin ray is nerve cord containing neurocoel.
- Notochord below nerve cord with chordal sheath enclosing vacuolated notochordal cells filled with homogeneous fluid.
- Ventral part of section contains two ovaries.
- Ovaries, enclosed in coelomic sac, contain several ova and are found from 25-51 segments. Pharynx, surrounded by atrial cavity, contains gill slits, epipharyngeal groove dorsally and endostyle ventrally.
- Two metapleural folds are seen ventro-Iaterally. In some sections midgut diverticulum or liver is also seen.
- Other structures seen are ventral vessel sub-endostyler coelomic caudal and coelomic space.
Identification: Since the section contains ova and all above characters, hence it is T.S. of female through ovaries of Amphioxus.
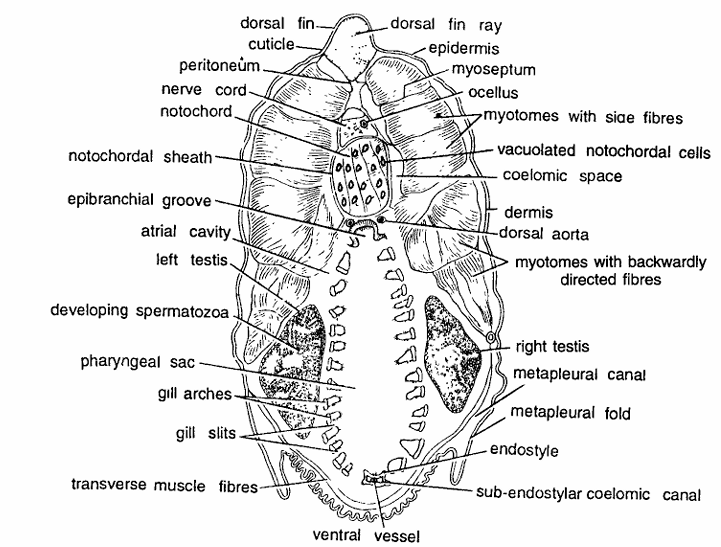
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Testes
Comments
- T.S. passing through testes shows body wall layers, nerve cord, notochord, large pharynx, etc.
- Body wall is composed of thin cuticle, thin epidermis and dermis and thick cut longitudinal segmental myotomes separated by myosepta.
- First four myotomes are quite thick and last two comparatively thinner.
- Muscle fibres in first three myotomes are slightly upwardly directed while in posterior three backwardly directed.
- Dorsal tin ray just below epidermis. Nerve cord containing neurocoel is present below the fin ray.
- Below the nerve cord is present notochord composed of chordal sheath enclosing vacuolated notochordal cells filled with homogeneous fluid.
- Pharynx is a large cavity and contains dorsal epipharyngeal groove, ventral endostyle and on sides several gill clefts and gill arches.
- Testes are found on both sides having several dot-shaped cut spermatozoa.
- Metapleural folds and metapleural canals are seen ventro laterally.
- Other structures seen are gill arches, peritoneum, transverse muscle fibres, sub-endostyler coelomic canal, coelomic spaces, dorsal aorta, septum and ocellus.
Identification: Since the section contains dot-shaped cut spermatozoa, and all above characters, hence it is T.S. of male through testes of Amphioxus.
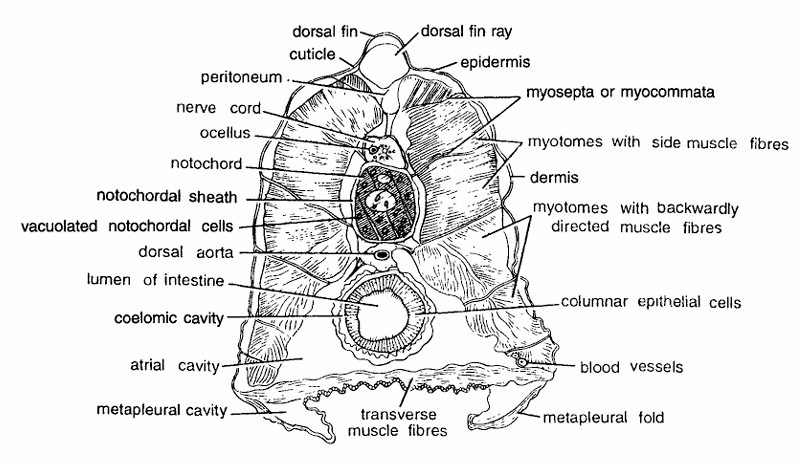
Amphioxus Slides : T. S. Passing Through Mid-gut or Intestine
Comments
- Intestine is found in posterior region. T.S. through intestine shows usual body wall, layers, nerve cord, notochord, intestine and metapleural folds.
- Body wall is composed of thin cuticle, thin epidermis, dermis and muscle layer.
- Muscle layer consists of alternating thick segmental myotomes separated by myocommata.
- Four myotomes forming anterior end are very thick while posterior last three myotomes are thinner.
- Muscle fibres in first three myotomes are directed slightly upwards while last three have backwardly directed muscle fibres.
- Dorsal fin ray is found below epidermis. Glandular nerve cord is found below dorsal fin ray. It encloses central canal or neurocoel.
- Notochord found below nerve cord is with vacuolated chordal cells. There is a single dorsal aorta below notochord.
- Ventral half of the section contains mid-gut, coelomic cavity and atrial cavity. Below coelom is well developed atrial cavity.
- Below atrial cavity transverse muscles and metapleural folds are seen.
- Mid-gut or intestine is found in the centre, composed of large endodermal columnar ciliated epithelial cells.
- Other structures seen in the section one ocellus, peritoneum, metapleural cavity, transverse muscle fibres, metapleural folds, blood vessels.
Identification : Since the section contains cut intestine, renal papillae and all above characters, hence it is T.S. of Amphioxus through intestine.
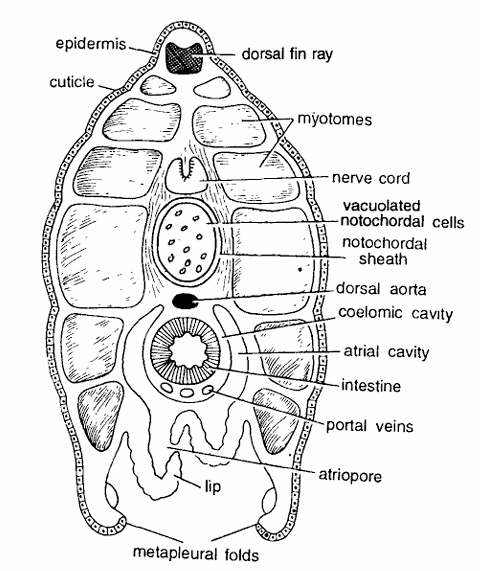
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Atriopore
Comments
- Animal narrows towards the posterior region. Hence T.S. passing through atriopore shows smaller sectIOn. In the section body wall layers, nerve cord, notochord, and atriopore are seen.
- Body wall comprises of thin cuticle, single-layered thin epidermis, thin dermis and segmental muscles or myotomes which are comparatively thinner and separated by myocommata.
- Dorsal fin ray is present below the epidermis.
- Nerve cord is found below 2 or 3 myotomes in the middle. It contains neurocoel.
- Notochord with notochordal sheath and vacuolated chordal cells is present below the nerve cord.
- Just below notochord is single dorsal aorta. Intestine shows smaller diameter and is composed of endodermal cells.
- It is surrounded by coelomic and atrial cavities.
- Few cut portal veins are also seen. Atrial cavity surrounds coelom and opens ventrally by a distinct atriopore, situated in front of the ventral fin.
- The two metapleural folds are distinctly seen.
Identification : Since this section contains atriopore and all above characters, hence it is T.S. of Amphioxus through atriopore.
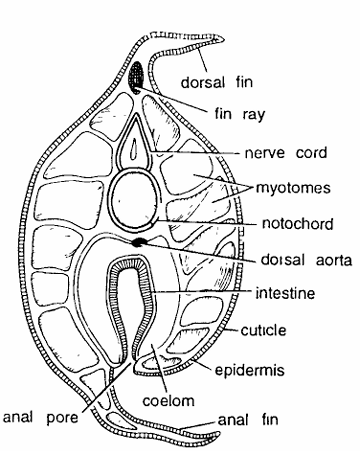
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Anal Region
Comments
- As the body narrows posteriorly the T.S. passing through anal region shows smaller diameter and it tapers at both the ends.
- Body wall is composed of thin cuticle, epidermis, dermis and myotomes alternating with myosepta.
- Dorsal fin ray is present below the pointed epidermis dorsally.
- Nerve cord is found below dorsal fin ray and first myotome.
- It has central canal. Notochord is found beneath the nerve cord.
- It has vacuolated chordal cells. Dorsal aorta is present beneath the notochord.
- Coelomic cavity enclosing intestine. Intestine opens to the exterior by the anus. Ventral fin is pointed in section.
Identification : Since the section contains anus and all above characters, hence it is T.S. of Amphioxus through anal region.
Amphioxus Slides : T.S. Passing Through Caudal Region
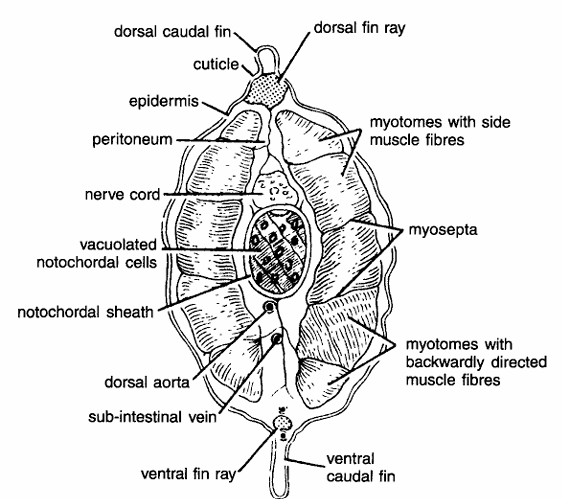
Comments
- Section through caudal region is somewhat smaller in size and without any opening.
- Body wall is composed of thin cuticle, single-layered epidermis, dermis and myotomes alternating with myocommata.
- Three upper myotomes have side muscle fibres while 2 posterior ores have backwardly directed fibers.
- Myotomes are separated by myosepta.
- Dorsal fin ray found at the base of dorsal fin below epidermis.
- Nerve cord with neurocoel lies below dorsal fin ray.
- Notochord with vacuolated chordal cells is found below the nerve cord.
- Caudal artery and vein appear below notochord.
- Alimentary canal, atrial cavity, coelom and metapleural folds are absent in this section.
- Caudal fin with fin ray is present posteriorly.
Identification : Since there is no opening, it is T.S. passing through the caudal region of Amphioxus.
