Introduction
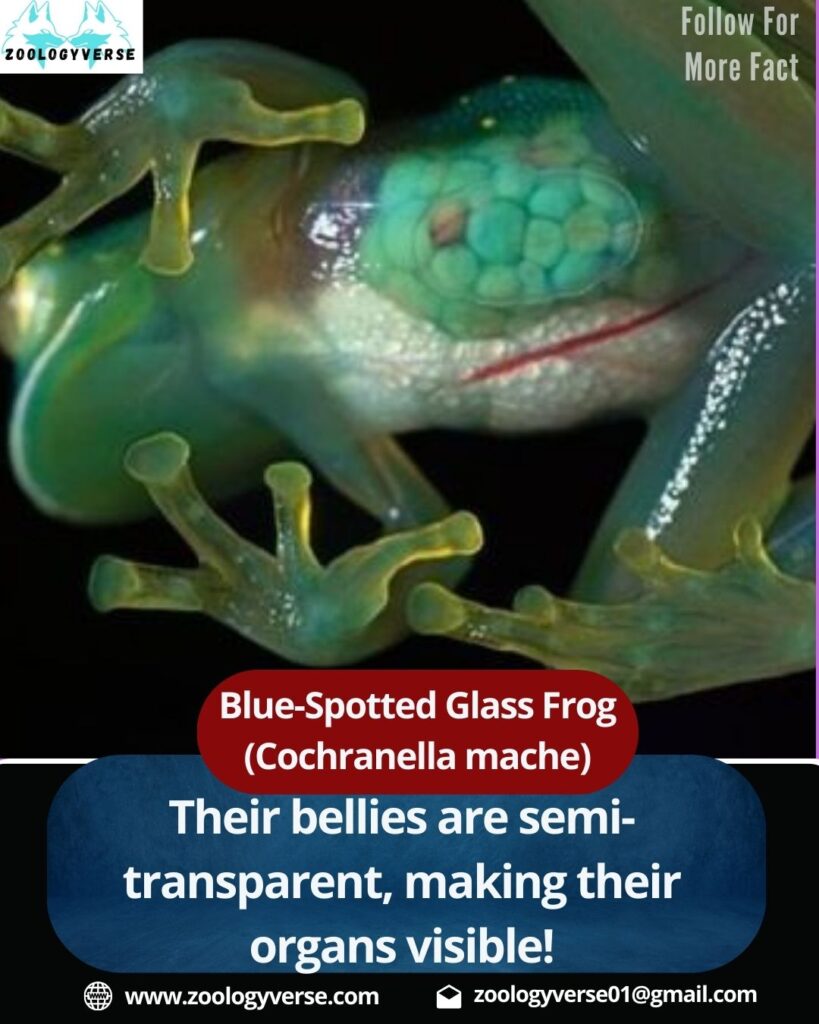
Deep within the lush rainforests of Ecuador and Colombia, a tiny yet mesmerizing amphibian thrives—the Blue-Spotted Glass Frog (Cochranella mache). This rare and unique frog species is known for its semi-transparent body and vibrant blue spots, setting it apart from other glass frogs.
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog is one of nature’s most mesmerizing amphibians. Known for its translucent skin and vibrant blue spots, this frog is a true wonder of the rainforest. In this article, we’ll explore its habitat, diet, behavior, and conservation status, along with some fascinating facts.
In this article, we will explore everything about this extraordinary frog, from its physical characteristics and habitat to its behavior, diet, reproduction, and conservation status. We’ll also cover some amazing facts and answer frequently asked questions about this species.
What is the Blue-Spotted Glass Frog?
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog belongs to the Centrolenidae family, commonly known as glass frogs due to their transparent or semi-transparent bellies. These frogs are arboreal (tree-dwelling) and are typically found near freshwater streams in tropical rainforests.
Scientific Classification
- Common Name: Blue-Spotted Glass Frog
- Scientific Name: Cochranella mache
- Family: Centrolenidae
- Order: Anura
- Habitat: Rainforests of Ecuador and Colombia
- Conservation Status: Vulnerable
This species was first identified in Ecuador, and its unique blue spots make it one of the most visually striking members of the glass frog family.

Physical Characteristics
1. Unique Coloration
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog has a vibrant green body with distinct blue speckles, making it one of the rarest glass frogs. Unlike other glass frogs, which have plain green skin, this species exhibits a spotted pattern that helps it blend into its surroundings.
2. Semi-Transparent Skin
Like most glass frogs, Cochranella mache has semi-transparent skin, allowing researchers to see its internal organs. This transparency provides natural camouflage, making it difficult for predators to spot them on leaves.
3. Size & Shape
- Length: 3–4 cm (1.2–1.6 inches)
- Weight: Very lightweight, typically less than 5 grams
- Body Shape: Slender with long limbs adapted for jumping and climbing
4. Unique Eyes
One of the most fascinating features of glass frogs is their large, forward-facing eyes with horizontal pupils. These specialized eyes provide excellent night vision, helping them detect predators and prey in the dark rainforest.
Habitat & Distribution
Where Does the Blue-Spotted Glass Frog Live?
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog is native to Ecuador and Colombia, specifically in the lowland rainforests near freshwater streams.
Preferred Habitat
- Tropical Rainforests – Moist, dense jungles with a high canopy.
- Near Freshwater Streams – They depend on clean water for reproduction.
- Altitude Range: Typically found between 200–800 meters above sea level.
These frogs are arboreal, meaning they spend most of their lives high in trees. They rarely come down to the ground, except when mating and laying eggs.
Threats to Their Habitat
- Deforestation due to logging and agriculture.
- Pollution affecting freshwater sources.
- Climate change leading to temperature shifts.

Diet & Feeding Habits
What Do Blue-Spotted Glass Frogs Eat?
Like most glass frogs, Cochranella mache is insectivorous, meaning it primarily feeds on small insects and other invertebrates.
Common Prey Items:
- Flies
- Ants
- Beetles
- Moths
- Spiders
How Do They Hunt?
- These frogs wait motionless on leaves and branches.
- They ambush their prey using their sticky tongues to capture insects in a split second.
- Their camouflage allows them to blend into the leaves, making it easier to catch unsuspecting insects.
Being nocturnal, they only hunt at night, when their prey is most active.
Reproduction & Behavior
Mating & Egg-Laying Process
- Mating Season: Blue-Spotted Glass Frogs mate during the rainy season when humidity is high.
- Egg-Laying: Females lay their eggs on the underside of leaves hanging over water.
- Parental Care: Unlike most amphibians, males guard the eggs from predators until they hatch.
- Hatching: When the tadpoles emerge, they drop directly into the water, where they develop before turning into adult frogs.
Male Vocalization
Male Blue-Spotted Glass Frogs produce soft, high-pitched calls to attract females and defend their territory from rival males.

Conservation Status & Threats
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog is classified as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Deforestation – Large-scale logging and agriculture are destroying its habitat.
- Pollution – Chemicals from farming and industry contaminate freshwater streams.
- Climate Change – Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns affect their environment.
Conservation Efforts
- Rainforest preservation programs in Ecuador and Colombia.
- Habitat protection laws to restrict logging and deforestation.
- Breeding programs in wildlife reserves to increase population numbers.
10 Amazing Facts About the Blue-Spotted Glass Frog
- Their bellies are semi-transparent, making their organs visible!
- They are nocturnal and only come out at night.
- Males protect their eggs, which is rare among frogs.
- They have a unique spotted pattern, unlike most other glass frogs.
- Their camouflage helps them avoid predators like birds and snakes.
- They are highly sensitive to water quality, making them indicators of environmental health.
- Some glass frogs have green bones, helping them blend into leaves!
- They communicate using high-pitched calls, which humans can barely hear.
- Tadpoles drop directly into the water when they hatch, a clever survival strategy.
- They are found only in select regions of Ecuador and Colombia, making them extremely rare.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Where can I find the Blue-Spotted Glass Frog?
This species is found in Ecuador’s rainforests, specifically in the Cordillera Mache-Chindul region, and in parts of Colombia.
2. Why are they called glass frogs?
They are called glass frogs because their bellies are semi-transparent, sometimes revealing their organs.
3. Are Blue-Spotted Glass Frogs poisonous?
No, these frogs are harmless to humans and do not produce toxins.
4. What do they eat?
They eat insects like flies, ants, moths, and beetles.
5. How can we help conserve this species?
Supporting rainforest conservation efforts, reducing deforestation, and protecting freshwater sources can help preserve their habitat.
The Blue-Spotted Glass Frog is a stunning yet fragile species that plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. With its unique coloration, nocturnal behavior, and fascinating reproductive strategies, this frog remains one of the most intriguing amphibians in the world.
However, due to habitat loss and environmental threats, its survival is at risk. By promoting conservation efforts and spreading awareness, we can help ensure that this incredible species continues to thrive in the wild.
Would you like to see more rare species featured on ZoologyVerse? Let us know in the comments! 🐸🌿

