Classification of Alytes : Midwife Toad
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Amphibia (Cold blooded. Scaleless glandular skin. Can live in water and land. Two occipital condyles, Heart three chambered)
- Order :- Anura or Salientia (Scaleless Amphibia. Tail, external gills and gill-silts absent. Both hind limbs and forelimbs well developed.)
- Suborder :- Opisthocoela (Vertebrae opisthocoelous, ribs free.)
- Family :- Discoglossidae (Tongue and eyelids present. Adults with ribs..)
- Genus :- Alytes
Geographical distribution of Alytes : Midwife Toad
Alytes is found in European countries. Miocene.
Habit and habitat of Alytes : Midwife Toad
Alytes is an amphibious toad.
General Characteristics of Alytes : Midwife Toad
- Commonly known as Midwife toad.
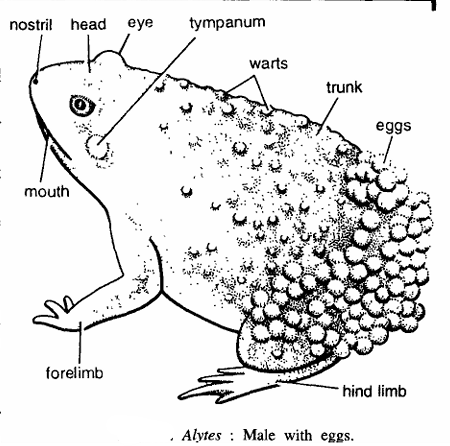
- Body measures 5 to 8 cm in length and divided into head and trunk.
- Body surface is warty and grey, brown, green or red coloured.
- Head contains large tympanum and protuberant eyes.
- Tongue is in the form of rounded non-protrusible disc.
- Males are without vocal sacs.
- Larva contains median spiracle.
- Upper jaw toothed, and transverse process of sacral vertebrae dilated.
- Vertebrae opisthocoelous. Adults have ribs.
- Fertilization and egg deposition external.
Special features
- The midwife toad has peculiar breeding habit. The male toad messages the cloaca of female with strokes of its toes for sexual stimulation and the female lays eggs in strings. The male sprays sperms over the eggs for fertilization of eggs. The male toad winds strings containing eggs around its posterior body and thighs and it goes in moist earth. Occasionally, the male toad comes in water for dip to moisten the eggs. When eggs develop into tadpole stage and are ready for hatching, the toad goes in water and larvae hatch. This shows extraordinary parental care.
Identification
Since this Anura has eggs on back and above features, hence it is Alytes.



