Introduction
Anguilla vulgaris, commonly known as the European eel, is a catadromous fish species belonging to the family Anguillidae. This species is renowned for its remarkable life cycle, involving long-distance migration from European freshwater habitats to the Sargasso Sea for reproduction. The European eel exhibits significant ecological, cultural, and economic importance, particularly in European regions where it is a staple in traditional cuisines and local fisheries.
Despite its resilience, Anguilla vulgaris faces critical challenges due to overfishing, habitat loss, and barriers to migration, which have led to drastic population declines. Its unique migratory behavior and adaptability make it a subject of considerable scientific interest and conservation efforts.
Classification of Anguilla Vulgaris (European Eel)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Osteichthyes (Bony fishes. Skin contains dermal scales. Paired lateral fins present. Gills, air bladder present. Cleavage meroblastic.)
- Sub-Class :- Actinopterygii (Modern fishes. Vertebrae amphicoelous. Caudal fin homocercal, Scales cycloid or ctenoid. Nostrils do not communicate with mouth cavity.
- Superorder : Teleostei (Bony fish proper)
- Order :- Anguillformes (Body long and slender. Air bladder with ducts. Gill openings small. Scales minute or absent. Dorsal. caudal and anal fins continuous.)
- Genus :- Anguilla
- Species :- vulgaris
Geographical distribution
- Anguilla vulgaris is widely distributed in Europe, North Africa, temperate Asia, North America, Mexico, West Indies, Australia and New Zealand. They are not found in Eastern Pacific and South Atlantic. Cretaceous to Recent.
- Native to European rivers, streams, and coastal waters.
- Found in a range extending from Scandinavia and the Baltic region to the Mediterranean and North Africa.
- Migrates to the Sargasso Sea in the Atlantic Ocean for spawning.
Habit and habitat
Anguilla is a fresh-water fish. It is a voracious feeder and catadromous fish and it can live for several hours out of water. The adult eels live in ponds, estuaries, rivers and coastal areas of the sea and damp grass or moss outside water.
- Habit:
- Omnivorous, feeding on aquatic insects, crustaceans, small fish, and detritus.
- Exhibits nocturnal activity and burrowing behavior for shelter and feeding.
- Habitat:
- Found in a variety of freshwater, brackish, and marine environments, including rivers, lakes, estuaries, and coastal waters.
- Juveniles inhabit freshwater habitats, while adults migrate to the ocean for reproduction.

General Characteristics of Anguilla Vulgaris (European Eel)
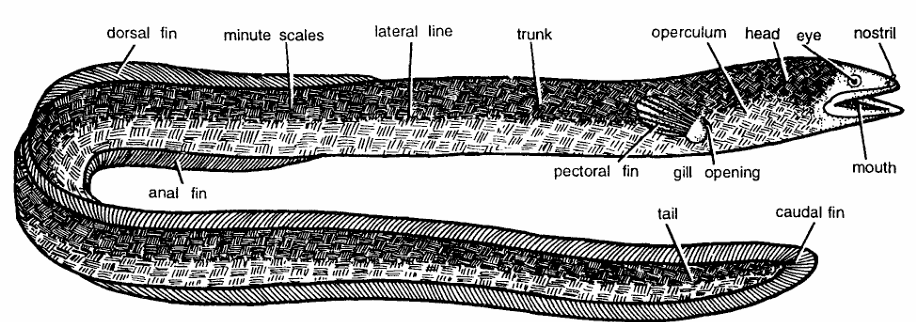
- Commonly known as eel, measuring 1.2 meters in length.
- Body is slender, elongated and snl:!ke like. Body divisible into head, trunk and tail.
- On each side operculum covers the gill slits. Head contains mouth, eyes and nostril.
- Dorsal fin, anal fin and caudal fin are joined together forming a continuous fin. Fins are supported by fin rays.
- Body is covered by minute scales embedded in the skin and arranged obliquely at right angles to one another forming a curious pattern.
- Maxillaries and palatopterygoid present, gill cleft separate and vertebrae greatly enlarged.
- Spines absent, gill openings small, air bladder has a ductus pneumaticus. Oviducts absent.
- Gills displaced posteriorly with 6 to 22 branchiostegal rays. There are no special accessory organs for breathing air. When on land, probably air is taken through skin.
Ecological Importance
- Food Web Dynamics: Plays a critical role in nutrient cycling and energy transfer between freshwater and marine ecosystems.
- Indicator Species: Acts as an ecological indicator due to its sensitivity to water quality and habitat changes.
- Prey and Predator Role: Serves as a food source for larger predators while regulating populations of smaller aquatic organisms.
Conservation Status of Anguilla Vulgaris (European Eel)
- Anguilla Vulgaris Classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- Threats include:
- Overfishing and illegal trade.
- Habitat destruction from dams, pollution, and land use changes.
- Climate change impacting migration routes and spawning habitats.
- Conservation measures:
- Establishing eel ladders and fish passes to facilitate migration.
- Implementing fishing regulations and habitat restoration projects.

Special features
- Eels have peculiar breeding habits and life-histories. Both the American and European eels, when about 60 cm long, put on breeding colours. The green European eel travels about 3,000 miles to spawn in hot waters of West Indies. Upon reaching the coastal waters, green colour changes
- to silver eyes are enlarged and gonads mature.
- The fish lays about 10 million eggs, which hatch into pelagic larvae called as Leptocephali. These larvae take homeward journey. On the contrary to present known work, Aristotle thought that they come from ‘entrails of earth’.
- Catadromous Migration: Migrates thousands of kilometers to the Sargasso Sea for spawning, a unique life cycle among fish species.
- Long Lifespan: Can live up to 20 years in freshwater before undertaking migration.
- Resilience: Highly adaptable to diverse habitats and environmental conditions.
- Economic and Cultural Importance: Prized in traditional cuisines and fisheries, particularly in Europe.
- Elongated Body Structure: Slender, snake-like body adapted for efficient swimming and burrowing
Identification
- Since this fish has continuous caudal, anal and dorsal fins and above features, hence it is Anguilla Vulgaris.
References
- IUCN Red List – Anguilla vulgaris
- FishBase – European Eel
- WWF – Conservation of European Eel
- Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF)
- ResearchGate – European Eel Migration and Ecology
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate

