Introduction
Barbus sarana, commonly referred to as the sarana barb or minnow, is a small to medium-sized freshwater fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae. Found across South and Southeast Asia, this species is a valuable component of aquatic ecosystems due to its role in nutrient cycling and as a food source for larger fish and other predators.
Its adaptability to diverse habitats makes it widespread in rivers, streams, and reservoirs. Known for its schooling behavior and fast swimming, Barbus sarana is often studied for its ecological importance and economic value in local fisheries.
Classification of Barbus sarana (Minnow)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Osteichthyes (Bony fishes. Skin contains dermal scales. Paired lateral fins present. Gills, air bladder present. Cleavage meroblastic.)
- Sub-Class :- Actinopterygii (Modern fishes. Vertebrae amphicoelous. Caudal fin homocercal, Scales cycloid or ctenoid. Nostrils do not communicate with mouth cavity.
- Superorder : Teleostei (Bony fish proper)
- Order :- Cypriniformes (Anterior vertebrae fused. Weberian ossicles present between air bladder and ear.)
- Family :- Cyprinidae (Jaws toothless. Teeth in pharynx.)
- Genus :- Barbus
- Species :- sarana
Geographical distribution
- Found in South and Southeast Asia, including countries like India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar, and Thailand.
- Populations inhabit river systems such as the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Mekong.
Habit and habitat
- Habit:
- Omnivorous, feeding on aquatic plants, algae, insects, and small invertebrates.
- Typically active during the day and exhibits schooling behavior for protection and foraging efficiency
- Habitat:
- Prefers clear freshwater rivers, streams, ponds, and reservoirs.
- Commonly found in shallow, slow-moving waters with sandy or muddy substrates.

General Characteristics of Barbus sarana (Minnow)
- Commonly called as Minnow or carp.
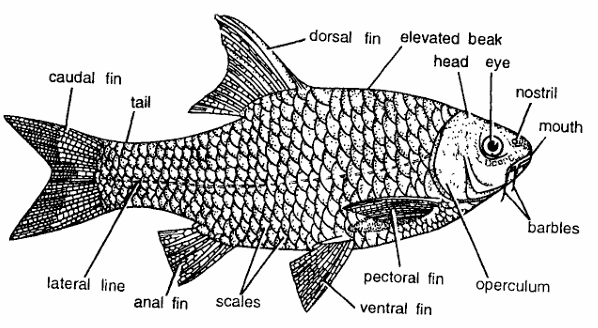
- Body of the fish is covered with large scales and is divided into head, trunk and tail.
- Head has an upward mouth without inner fold, small barbels, large eyes without adipose eye lid and devoid of scales. Head contains nostril.
- Lips thin without plicae or papillae; upper jaw bordered only by premaxillae.
- Pharyngeal teeth in one to three rows, never more than eight teeth in anyone row.
- Profile of the back is elevated. Inter-orbital space convex. Operculum and lateral line present.
- Fins are whitish or yellowish. Dorsal fin is opposite to anal fin and contains spine-like rays. Caudal fin forked. Pectoral and ventral fins present.
- Operculum is stout with golden colour.
- Air bladder divided into right and left lobes by a constriction and enclosed in an osseous capsule.
Ecological Importance
- Trophic Role: Acts as both prey and predator, maintaining food web balance in freshwater ecosystems.
- Nutrient Cycling: Plays a role in recycling nutrients by consuming detritus and algae.
- Indicator Species: Sensitive to water quality changes, making it a good indicator of ecosystem health
Conservation Status
- Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN due to its wide distribution and adaptability.
- However, threats include:
- Habitat loss due to dam construction, deforestation, and water pollution.
- Overfishing in certain areas for food and local markets.
- Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration and sustainable fishing practices.

Special features
- Adaptability: Can thrive in a variety of freshwater habitats, including polluted or low-oxygen waters.
- Economic Value: Widely consumed as food and contributes to small-scale fisheries.
- Reproductive Behavior: Spawns during monsoon seasons, with high fecundity ensuring population resilience.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Often brightly colored, making it an attractive species in ornamental fish trade.
- Schooling Behavior: Exhibits group swimming, reducing predation risk and enhancing foraging success.
Identification
- Since this fish has scaleless head, simple lips and above features, hence it is Barbus.
References
- FishBase – Barbus sarana
- IUCN Red List – Barbus sarana
- ResearchGate – Ecology of Barbus species
- GBIF – Global Biodiversity Information Facility
- National Fisheries Development Board (India)
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate

