Introduction
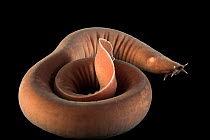
Bdellostoma is a genus of jawless marine creatures belonging to the class Myxini, commonly referred to as hagfish. These primitive chordates are often considered living fossils due to their retention of ancestral vertebrate traits. Similar to their close relatives in the genus Myxine, Bdellostoma exhibits an eel-like body and lacks jaws, paired fins, and true vertebrae.
Primarily scavengers, Bdellostoma species play an essential role in deep-sea ecosystems by consuming decaying organic matter. They are known for their ability to secrete copious amounts of slime when threatened, a unique adaptation that deters predators and aids in their survival.
Classification of Bdellostoma
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Acraniata (No head, cranium or brain)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Agnatha (Jaws and paired appendages absen)
- Class :- Cyclostomata (Mouth circular, suctorial, without jaws)
- Order :- Myxiniformes (Mouth without funnel, with 8 tentacles. Gills 10 to 14 pairs. Branchial basket feebly developed.)
- Family :- Myxinidae
- Genus :- Bdellostoma
Geographical distribution
- Bdellostoma is distributed in the Pacific coasts of North and South America, South Africa and New Zealand.
- Prefer temperate and cold waters, often inhabiting deep-sea environments.
Habit and habitat
- Bdellostoma is found buried in mud and sand during day; otherwise it is nocturnal feeder and ectoparasitic and highly adapted for sucking.
- Habit:
- Scavengers, feeding on dead or dying marine animals.
- Can burrow into carcasses or sediment for feeding and shelter.
- Habitat:
- Lives in deep-sea environments, typically in muddy or sandy substrates.
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to over 1,000 meters.
Comments on Bdellostoma
- Bdellostoma is also commonly called as hagfish.
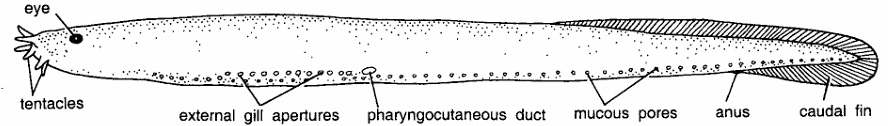
- Body elongated, soft, eel-like without scales and divided into head, trunk and tail.
- Teeth are well developed. Jaws are completely absent.
- Eyes are rudimentary, skin sensory. Eight sensory tentacles are found around mouth. Single nostril is very close to the mouth.
- Gills are modified into pouches which are 6 to 14 in number and they open independently.
- Entire body contains double rows of mucous glands. On ventro-Iateral side is row of mucous pores.
- Blood is isosomatic with sea water. Dorsal tin continuous with caudal tin.
- Egg is yolky with partial cleavage leading to the formation of an embryo perched on a mass of yolk.
- Single pineal eye is present at the top of head.
- Nostril is hermaphroditic and protandrous.
Ecological Importance
- Economic importance : Hagfishes damage fish caught in nets. Sometimes hagfishes enter into the body of other fishes and eat entire soft parts leaving only a bag of skin and the bones.
- Nutrient Recycling: Plays a vital role in the decomposition of organic matter in marine ecosystems.
- Food Web Role: Acts as prey for larger marine predators, such as sharks and larger fish.
- Ecosystem Health Indicator: Presence indicates the health of benthic ecosystems.
Conservation Status
- Not currently listed as endangered, but populations are affected by human activities such as deep-sea trawling and overfishing.
- Harvested in some regions for their skin (marketed as “eel leather”) and sometimes as food.
Special features
- It has the same phylogenetic importance as that of Myxine. Pronephros persistent in the adult but the functional kidney is mesonephros.
- Slime Secretion: Produces large quantities of slime as a defense mechanism, clogging the gills of predators.
- Simple Body Plan: Lacks jaws, paired fins, and a vertebral column but possesses a notochord for structural support.
- Feeding Adaptations: Uses a set of keratinous teeth-like structures to rasp flesh from carcasses.
- Regenerative Capabilities: Demonstrates efficient tissue regeneration, aiding in survival in harsh environments.
- Survival Skills: Can endure long periods without food and thrive in low oxygen conditions.
Identification
- Since the. animal is without jaws and with 8 tentacles and above features, hence it is Bdellostoma.
References
- Encyclopedia of Life – Bdellostoma
- Marine Species Identification Portal
- World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS)
- ScienceDirect – Deep-Sea Scavengers
- National Geographic – Hagfish Biology
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate


Thanks a lot! 🎉