Corvus splendens, commonly known as the House Crow, is one of the most familiar urban birds across South Asia. Highly intelligent and adaptable, this species thrives in human-dominated environments such as towns, villages, coastal areas, and agricultural landscapes. Recognized by its glossy black plumage, grey neck, and harsh cawing calls, the House Crow is an opportunistic omnivore that feeds on grains, insects, fruits, refuse, and small animals. Its strong social behavior, problem-solving ability, and close association with human settlements have enabled it to expand its range to parts of East Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. Corvus splendens plays a significant ecological role in waste removal but can also act as a pest or invasive species in some regions.
Classification of Corvus Splendens (Crow)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Aves (Biped and feathered vertebrates.)
- Sub Class :- Neornithes (True birds. Metacarpals fused.)
- Super Order :- Neognathae (Modern birds. no teeth. sternum keeled.)
- Order :- Passeriformes (Perching bird. Toes 3 in front and behind.)
- Genus :- Corvus
- Species :- splendens
Geographical distribution of Corvus Splendens (Crow)
- Corvus splendens is found everywhere in India.
Habit and habitat of Corvus Splendens (Crow)
- It is the most common, most familiar, most intelligent and boldest bird, living on trees in towns, villages and gardens. It feeds on any thing from dead meat to any eatable left on the table, i.e., bread, butter, fruits and other preparations. Always around human habitat.
General Characteristics of Corvus Splendens (Crow)
- Commonly called as House Crow
- Adult crow 32 to 42 cm in length.
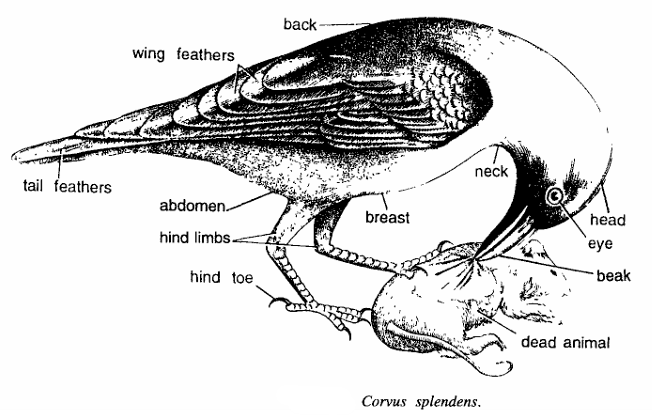
- Body divisible into head, neck, back, breast and abdomen.
- Head contains eyes and beak. Beak adapted for tearing and cutting.
- Neck and breast are grey, but back and plumage are glossy black.
- Eyes are large and beak stout and elongated. Tail feathers are elongated. Wing feathers folded dorsolaterally.
- Feet adapted for perching, 3 toes in front and 1 behind.
- Young naked and blind at hatching, require feeding and parental care eating rats and dead animals before becoming independent.

Ecological Importance
Corvus splendens, commonly known as the house crow, is a highly adaptable and widespread bird found in South Asia and parts of the Middle East. It plays an important role in the ecosystems it inhabits, contributing to biodiversity and functioning in several ecological processes. Here are the key ecological roles and importance of the house crow:
1. Scavenger and Decomposer
- Waste Disposal: House crows are opportunistic feeders and scavengers, feeding on a wide range of food items, including garbage, carrion, and leftover food. By consuming organic waste, they help in waste disposal, reducing the buildup of decaying matter and preventing the spread of disease.
- Decomposition Contribution: As scavengers, they contribute to the breakdown of organic materials, helping in nutrient cycling and enriching the soil.
2. Predator and Pest Control
- Insect Control: House crows feed on a variety of insects, including agricultural pests like locusts, beetles, and caterpillars. Their predation helps to control pest populations that could otherwise damage crops and plants.
- Small Vertebrate Predation: They also prey on small vertebrates, such as rodents, reptiles, and amphibians, helping to regulate their populations and maintain a balanced ecosystem.
3. Seed Dispersal
- While primarily omnivorous, house crows occasionally feed on fruits and berries. In doing so, they may inadvertently disperse seeds through their droppings, facilitating plant regeneration and the spread of various plant species.
4. Nesting in Urban and Forested Areas
- House crows are known for nesting in both urban and natural habitats, often building nests in trees, buildings, and other elevated structures. Their nesting behavior can contribute to the structural complexity of ecosystems, creating habitats for other species and contributing to biodiversity.
5. Indicator of Environmental Health
- House crows are considered bioindicators of environmental health. Their presence and population dynamics can reflect the condition of the environment, including the availability of food resources, human impact, and changes in habitat quality.
- For example, their abundance in urban areas may indicate pollution or habitat modification, while declines in their numbers could suggest deteriorating environmental conditions.
6. Role in Food Webs
- As omnivores, house crows are an integral part of the food web. They serve as both predators and prey, supporting higher-level predators such as birds of prey and larger mammals, while also controlling populations of insects, rodents, and smaller vertebrates.
7. Cultural and Ecological Adaptability
- House crows are highly adaptable and have thrived in human-modified environments. Their ability to live in diverse habitats, including urban, suburban, and rural areas, allows them to play a role in the ecological balance of both natural and human-dominated ecosystems.
- Their behavioral flexibility, such as using tools to obtain food and their intelligence in foraging, contributes to the stability of their ecological niche.
8. Seedling and Plant Damage
- While crows contribute to seed dispersal, they can also pose a threat to certain crops and plants by eating seeds, fruits, or young seedlings. This behavior may affect the growth of specific plant species, although this is generally a minor negative impact in the broader context of ecosystem functioning.
Conservation Considerations
- House crows are highly adaptable, and their population is not under significant threat. However, in areas where their numbers have surged due to urbanization and human activity, they may sometimes be seen as pests. Managing their population is important in balancing their positive ecological contributions with any potential negative impacts on crops or other species.
Corvus splendens plays a crucial role in ecosystems through its scavenging, pest control, seed dispersal, and contribution to biodiversity. By helping in waste management, regulating insect and small vertebrate populations, and creating habitats for other species, house crows are vital for maintaining the ecological balance in both urban and natural environments.

Special Features of Corvus Splendens (Crow)
- The house crow acts as efficient municipal scavenger. It destroys locusts and other injurious insects but it also destroys the crop and fruits in orchards. The house crow builds nests of sticks. They roost communally in large flocks. They are also a menace to the eggs and infants of other birds. Whenever any fellow crow dies, several crows assemble. It is very intelligent and danger avoiding bird.
Identification
- Since the above bird has raised head and above features, hence it is Corvus splendens.