Introduction
The genus Heloderma includes venomous lizards like the Gila monster (H. suspectum) and the Mexican beaded lizard (H. horridum). These lizards are native to arid and semi-arid regions of North and Central America. Known for their slow movements and bead-like skin texture, Heloderma species are unique among lizards due to their venomous nature, which is used primarily for defense.
Classification of Heloderma (Gilla Monster)
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Definite head, Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Tetrapoda (Paired limbs, lungs, cornified skin and bony skeleton.)
- Class :- Reptilia (Scaly vertebrates. Right and left aortic arches present. Single condyle. Pulmonary respiration. Embryo with amnion and allantois.)
- Sub Class :- Diapsida (Skull with two temporal openings separated by post-orbital and squamosal.)
- Order :- Squamata (Lizards and snakes with horny epidermal scales or shields. Quadrate bone movable. Vertebrae procoelous. Anal opening transverse.. Vertebrae amphicentrous.)
- Sub-order :- Iguania (Lizards. Body slender, limbs 4. Pterygoid in contact with quadrate. Eyelids movable.)
- Family :- Helodermidae (Poisonous lizard. Fleshy bifid tongue.)
- Genus :- Heloderma
Geographical distribution
- Heloderma is found in deserts of Mexico and U.S.A.
Habit and habitat
- Heloderma lives in dry places under rocks and in burrows. It is a clumsy, sluggish animal which feeds on snake eggs and lizards.
General Characteristics of Heloderma (Gilla Monster)
- Commonly called as Gilla monster.
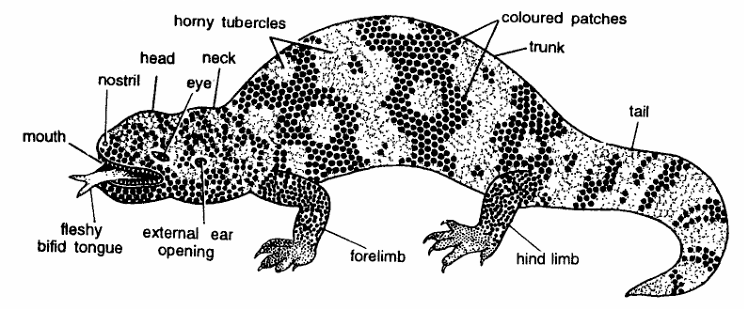
- Body measuring about 60 cm, is covered with ugly tubercles and divided into head, neck, trunkand tail.
- Body contains black and orange scales forming coloured patches. Dorsal scales are bead-like over bony tubercles (osteoderms). Ventral scales flat.
- Head is short, stout having eyes, nostrils and a wide mouth. External ear opening present behind eyes.
- Teeth pleurodont, fang-like and contain labial poison glands which open on outer ‘gum’ of lower jaw.
- Tongue is fleshy and bifid.
- Trunk and tail stout and rounded.
- Forelimbs and hind limbs are short, powerful and well developed. It is capable of swift movement.
- Digits are clawed.
- Heloderma lays eggs in the nest formed in sandy soil.
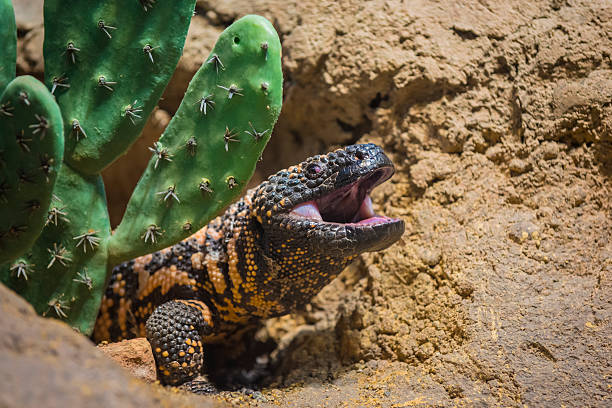

Ecological Importance
- Predator Role:
- This species are opportunistic predators, feeding on bird eggs, small mammals, insects, and carrion.
- By consuming eggs, they indirectly influence bird and reptile population dynamics.
- Seed Dispersal: Occasionally consuming fruits, these lizards contribute to seed dispersal in their habitats.
- Ecosystem Health Indicators: Their sensitivity to environmental changes makes them valuable indicators of habitat health and biodiversity.
Conservation Status
- Current Status of Species:
- H. suspectum (Gila Monster): Near Threatened due to habitat loss and illegal collection.
- H. horridum (Mexican Beaded Lizard): Near Threatened, facing similar threats.
- Threats:
- Habitat destruction due to urbanization and agriculture.
- Poaching for the illegal pet trade.
- Persecution due to misunderstanding of their venomous nature.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Legal protections under local and international laws, including listing in CITES Appendix II.
- Habitat preservation and restoration initiatives.
- Public awareness campaigns to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
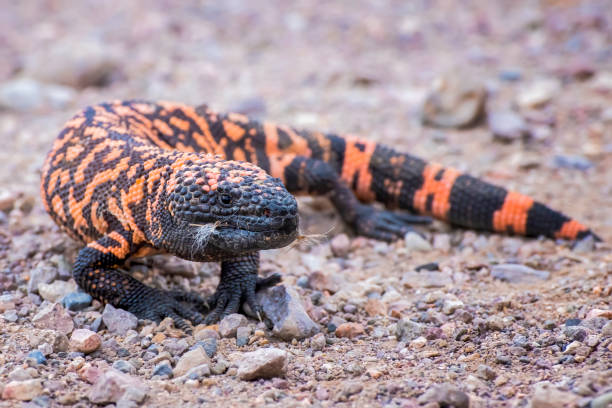

Special features
- Heloderma is the only poisonous lizard. The poison apparatus comprises of a modified sublingual salivary gland that secretes a poisonous fluid. Poison glands open on outer gum of lower jaw. Venom is potent; bite is fatal to small animals, and rarely to man.
- Venomous Nature: Heloderma lizards are among the few venomous lizards. Their venom, delivered through grooves in their teeth, is primarily used for defense.
- Bead-Like Skin: Their thick, bumpy skin resembles beads, providing protection and camouflage in arid environments.
- Slow Metabolism: These lizards have a low metabolic rate, allowing them to survive on infrequent meals.
- Defensive Behavior: Rather than attacking, they rely on warning displays like hissing and biting as a last resort.
- Medicinal Research: Proteins in their venom have inspired drugs for treating diabetes, such as exenatide, showcasing their biomedical significance.
Identification
- Since the lizard has bead-like scales, tubercles, coloured patches, stout trunk and above features, hence it is Heloderma.
References
- IUCN Red List – Heloderma
- National Geographic – Gila Monster
- Smithsonian National Zoo – Beaded Lizards
- CITES – Heloderma Conservation
- Wikipedia – Heloderma
- Zoology Practical Vertebrate

