Classification of Torpedo : Electric Ray
- Phylum :- Chordata (Dorsal tubular nerve cord, notochord and gill-slits present.)
- Group :- Craniata (Cranium with brain present.)
- Sub phylum :- Vertebrata (Vertebral column present.)
- Division :- Gnathostomata (Jaws and paired appendages present.)
- Super Class :- Pisces (Paired fins, gills and skin with scales.)
- Class :- Chondrichthyes (=Elasmobranchii) (Endoskeleton cartilaginous. Scales usually placoid. Notochord rudimentary, Spiral valve in intestine, opercula absent)
- Sub-Class :- Selachi (Sharks and rays, Gills in separate clefts, cloaca present)
- Order :- Hypotremata(=Batoide) (Gills-slits ventral, Spiracles Present, Dorsal Fin on tail, if present, Vertebrae tectospondylous.)
- Family :- Torpidinidae (Trunk forms a broad and smooth disk, contains electric organs.)
- Genus :- Torpedo (Electric ray)
Geographical distribution of Torpedo : Electric Ray
Torpedo has been reported from the Mediterranean, Atlantic and Indian Oceans, Red Sea, Pacific Ocean, East Indies, Tasmania, China, Japan, South Africa, North and South America as well as Australia. Upper Jurassic to Recent.
Habit and habitat of Torpedo : Electric Ray
Torpedo or Astrape is a marine fish, found on flat, sandy or muddy bottom at a depth of 40 to 50 fathoms. It is carnivorous.
General Characteristics of Torpedo : Electric Ray
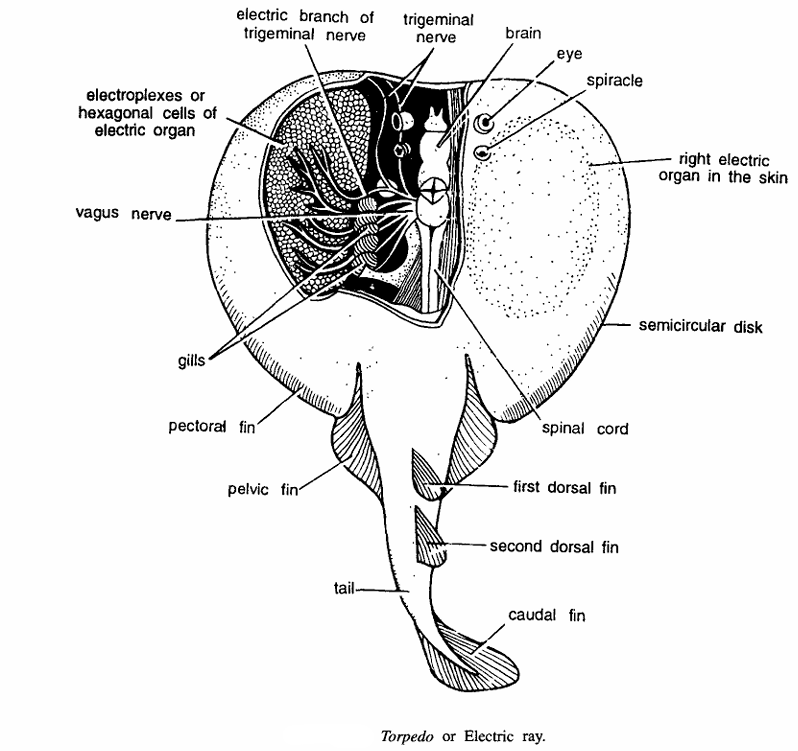
- Commonly known as Electric ray because of the presence of a pair of electric organs, one on either side of the body between head and the pectoral fins
- Body is regionated into anterior semicircular disk supported by endoskeleton and posterior tail. Fish measures 60 to 90 cm a,cross the widest part of the disk and the whole body has brown background which is ornamented with beautiful irregularly shaped, magenta-coloured spirals and spots.
- Semicircular region is supported by branched prenasal rostrum and laterally by branched pre-orbital cartilages. Branches radiate towards periphery.
- Disk is bordered by pectoral fins.
- Skin is smooth, non-tuberculate and without scales.
- Eyes and spiracles are closely placed above electric organs dorsally.
- Mouth is transverse and ventrally situated.
- Tail is thick and short with two dorsal fins, a caudal fm and two lateral folds of skin. Pelvic fins are just beneath the lower margin of the pectoral fin.
- Gill-slits on the ventral side.
- Viviparous and produces live youngs.
Special features
- Torpedo contains a pair of large electric organs between margins of pectoral fins and head. These organs are considered as modifications of the adductor mandibulate and constrictor muscles and supplied by vagus and trigeminal nerves from vagus and trigeminal nerves from electric lobe of the medulla
- Each electric organ is composed of hexagonal cells called as electroplaxes which are filled with jelly-like fluid and arranged vertically like prisms between upper and lower surfaces. Upper surface corresponds to anode and lower surface with the cathode. Thus, electric current of 50 to 60 volts passes from upper positive to lower negative surface. After fish has discharged electricity, some rest is required for further discharge. These are offensive and defensive organs and fishermen get electric shocks from captured electric rays.
Identification
Since this fish has 2 bulging electric organs and above features, hence it is Torpedo.



