DEVELOPMENT OF FROG
Frog : Structure of Ovum
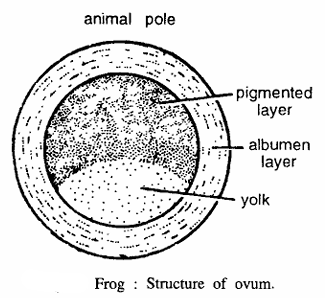
Comments
- The ovum is rounded in shape and covered by albumen layer, chorion and vitelline membrane.
- It measures 1.6 rom in diameter
- One half of the zygote is pigmented black called animal hemisphere and the remainder is almost white.
- Vitelline membrane swells up on the exposure to water. The interspaces contain minute plants, which give oxygen by their manufacture of food to the embryo.
- Cytoplasm of the egg contains yolk, nucleus, polar body and vitelline membrane.
- Blackish brown pigment granules of melanin assemble at future animal hemisphere forming a superficial pigmented layer.
- Centre of the pigmented area is the animal pole and the opposite end is the vegetal pole.
- Soon after fertilization the embryo rotates within the vitelline membrane so that the animal hemisphere is the uppermost.
Identification : Since the egg contains pigmented hemisphere towards animal pole, hence it is ovum of frog.
Frog : V.S. Passing Through Blastula
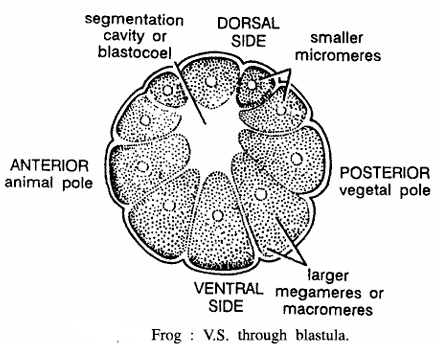
Comments
- Egg cleaves and forms blastula at 8-cell stage
- Blastula contains a blastocoel cavity surrounded by unequal blastomeres.
- Smaller blastomeres are called as micromeres, found in upper half and contain dark pigments.
- blastomeres are called as macromeres, found in more than lower half and laden with yolk.
- Lower side or vegetal hemisphere is composed of large yolky megameres.
- Because of their large size the blastocoel is excentric lying towards the animal pole.
Identification : Since the egg contains blastocoel and above features hence it is V. S. through blastula of frog.
Frog : V.S. Passing Through Gastrula

Comments
- Gastrulation is a rearrangement of cells already present in the blastula. This completely reorganizes embryo. During this process three germinal layers are formed
- Future prospective organ forming .cells are organized at their proper places at gastrula stage. Gastrulation occurs by epiboly, blastopore involution and invagination. During this process mesodermal and notochordal cells migrate inside, forming roof of archenteron.
- Gastrula has three germinal layers-namely, ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm from which various organs are derived. Section shows dorsal side, ventral side, animal pole and vegetal pole.
- Other structures seen in section are dorsal lip of blastopore, yolk plug, ventral lip of blastopore, notochordal cells and neural plate. The blastocoel is reduced due to the development of archenteron.
- Ectoderm gives rise to epidermis, cutaneous glands, nervous system, eye parts and lining of mouth cavity and cloaca. Endoderm forms lining of alimentary canal, liver, pancreas, lung and urinary bladder.
- Mesoderm gives rise to musculature, connective tissue, vascular system, genital organs, excretory organs, skeleton and notochord.
Identification : Since the section shows 3 germinal layers and above features, hence it is V. S. through gastrula of frog.
Frog : Tadpole Larva Whole Mount
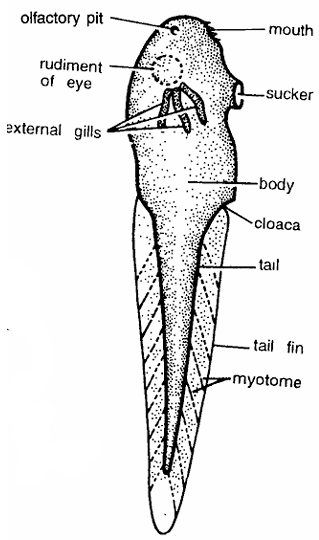
Comments
- Egg hatches into tadpole larva within 48 hours.
- It is whitish with dark pigment granules and 5 to 6.5 mm long.
- Larva is differentiated into body and tail with tail tin.
- Larva contains rudiments of eyes, olfactory pit, gill clefts, stomodaeum, cloaca and myotomes.
- Mouth contains horny jaws or horny teeth. Larva feeds on vegetation. Intestine is coiled.
- There are three pairs of external feathery gills which act as functional respiratory organs. Tadpole larva metamorphoses into adult.
Identification : Since the larva contains 3 pairs of gills and above features, hence it is whole mount of tadpole larva of frog.
Frog : Tadpole T.S. Passing Through Eyes
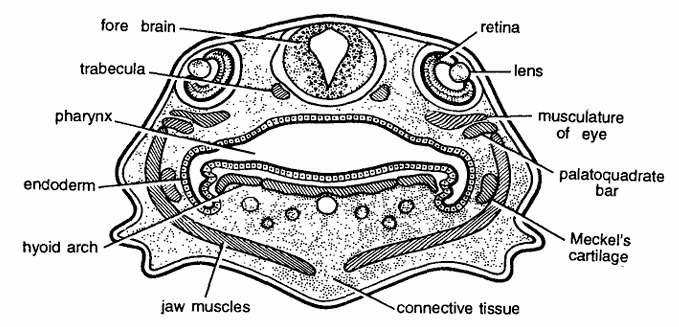
Comments
- Eyes are most conspicuous and portuberant structures and they begin to develop very early. Eyes develop from optic vesicles, which originate from a pair of diverticula given from thalamencephalon on each side. Below forebrain is trabecula.
- Section shows a pair of large eyes on the sides of forebrain. Each eye is composed of eye muscles, lens and sensory layer of retina.
- Other structures seen in section are jaw muscles, large pharynx, palatoquadrate bar, Meckels cartilage, hyoid arch, connective tissue and epidermis.
Identification : Since the section contains eye, hence it is T. S. tadpole of frog through eyes.
Frog : Early Tadpole T.S. Passing Through Ears
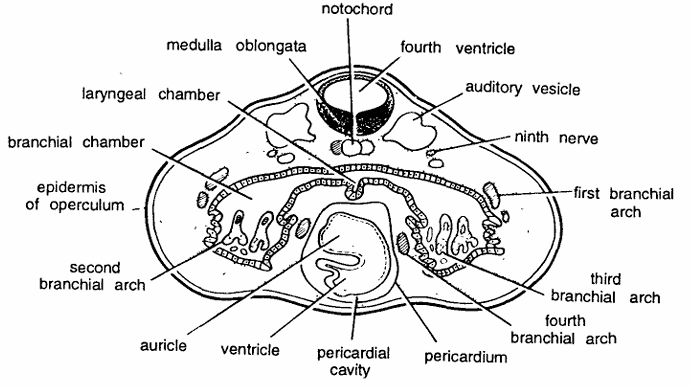
Comments :
- Ears develop as a pair of auditory pits from epiblast on sides of hindbrain
- Auditory pits become vesicle like called auditory vesicle and enclose the middle ear. Semicircular canals develop as outgrowths from the wall of auditory vesicles.
- Auditory vesicles develop at early tadpole stage and found on dorsal side of the section. Between two auditory vesicles is situated the medulla oblongata, enclosing IV ventricle. Beneath medulla oblongata the notochord is present.
- Lower portion of the section contains large pharynx, laryngeal chamber, branchial arches pericardial cavity and pericardium, enclosing developing auricle and ventricle.
- Other structures seen are first, second, third and fourth branchial arches, epidermis of operculum, news and ectoderm.
Identification: Since the section contains auditory vesicle and above features hence it is T.S. through ear of early tadpole of frog.
